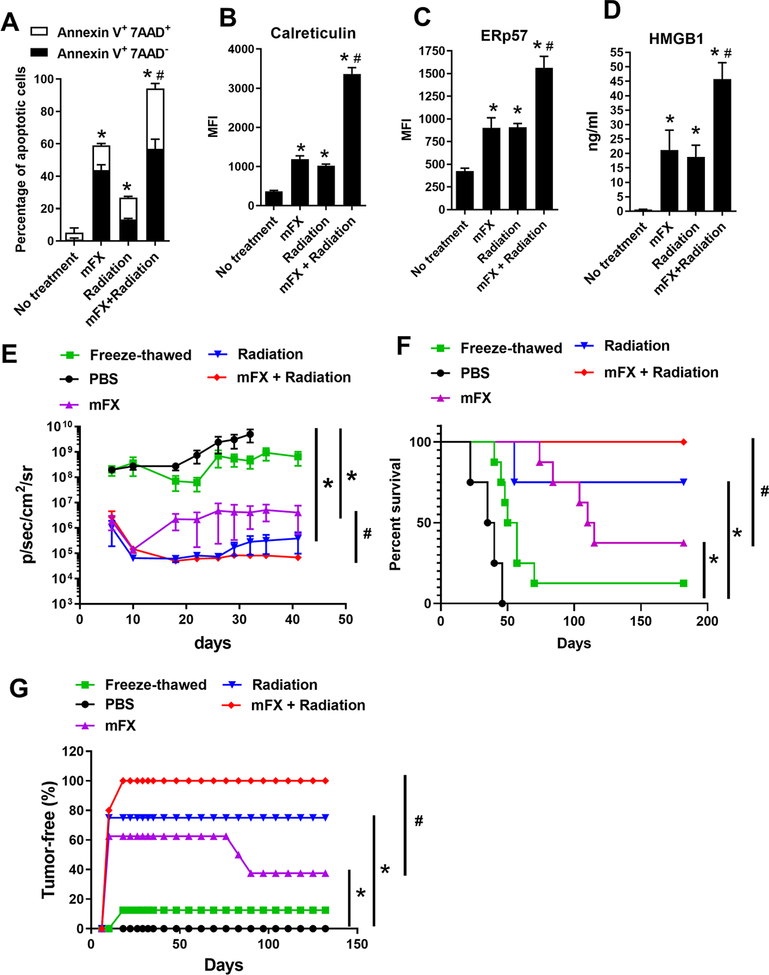
Figure 2. Enhanced ICD induced by combination of radiation and mFX.
KCKO-luc cells were treated or not treated with mFX (24 hours), radiation (6 Gy on day 0, 1, 2 and 3) or both in combination (radiation + mFX). (A) Apoptosis was determined by annexin V and 7-aminoactinomycin D (7-AAD). Early apoptotic cells were stained as annexin V positive and 7-AAD negative; late apoptotic cells stained as both annexin V and 7-AAD positive. (B, C) Cell surface calreticulin (B) and ERp57 (C) were stained and determined by flow cytometry. (D) HMGB1 secretion in culture medium was determined by ELISA. Data shown in (A-D) are mean ± SEM from three independent experiments and analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett post-test. *, p<0.05, compared with no treatment group; #, p<0.05, the combination was compared to mFX treated group. (E-G) KCKO-luc cells treated with mFX, radiation, combination of radiation and mFX, or freeze-thawed were inoculated s.c. into C57BL/6J mice. After 7 days, mice were re-challenged with live KCKO-luc cells in pancreas tail. (E) Tumor growth curve based on IVIS imaging. Data shown are mean ± SEM (n=5–8 mice/group). *p<0.05, compared with mFX treatment group by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett post-test. (F) The Kaplan Meier survival curve. (G) Percentage of tumor-free mice determined by IVIS and analyzed by log-rank(Mantel-Cox) test. *, p<0.05, compared with PBS group; #, p<0.05, the combination was compared to mFX treated group.