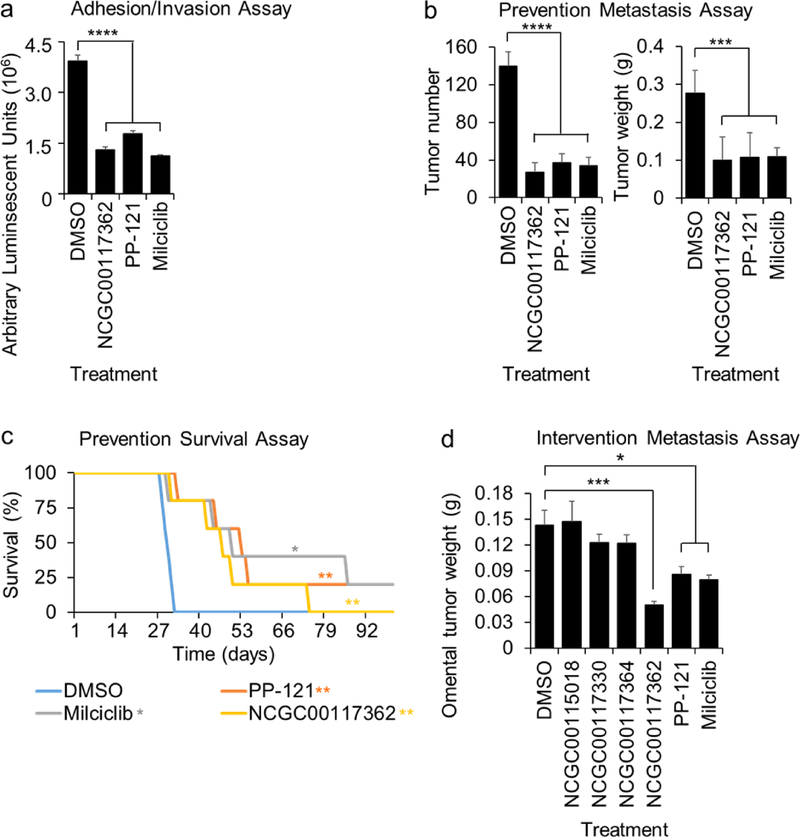
Figure 4. Activity of hit compounds in in vivo biological assays.
a-c. in vivo screens (adhesion/invasion and prevention metastasis assay). The compounds were tested at a 5μM dose. a. In Vivo Adhesion/Invasion Assay. Luciferase-labeled ID8p53−/− cells (5 million) were mixed with the indicated compound and injected into C57BL/6 mice. The mice were sacrificed at 16h and the luciferase signal in the omentum was measured. b-c. Five million Ovcar5 ovarian cancer cells were injected i.p. with NCGC1177362, PP-121 or Milciclib (5 μM), and i.p. treatment repeated 48 and 96 h post-cancer cell injection (3 total treatments: 10 mg/kg or equal volume of DMSO, n=5). b. In Vivo Prevention Metastasis Assay. Forty-five days post cancer cell injection the weight and number of tumors was determined (Mean+/− standard deviation). c. In Vivo Prevention Survival Study. Mice were sacrificed once they showed signs of distress, and Kaplan–Meier curves were calculated. d. In Vivo Intervention Metastasis Assay. 21 days post cancer cell injection the mice were i.p. treated daily with NCGC00117362, PP-121 or Milciclib (5mg/kg/day) and sacrificed 10 days later. The omental tumor weight was determined (mean+/− standard deviation). *, p<0.05. **, p<0.01. ***, p<0.001. ****, p<0.0001, n=5. DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide.