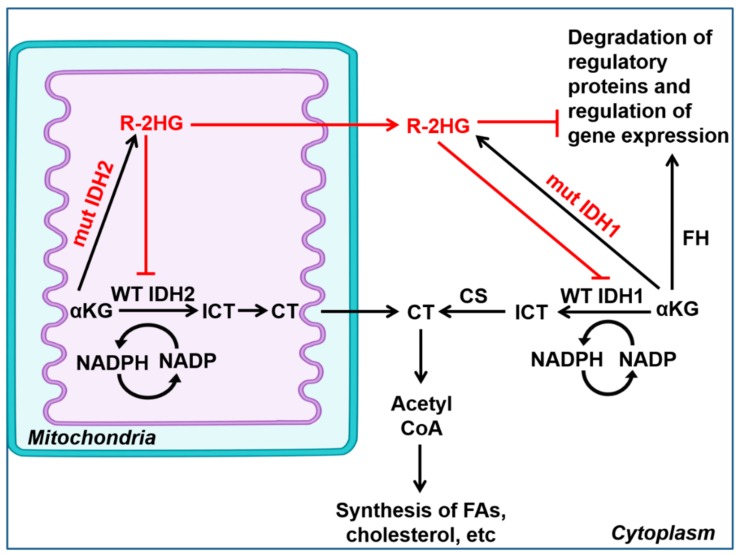
Figure 2.
Schematic presentation of the difference in cellular pathways of wild-type and mutated IDH1/2 enzymes during reverse reductive carboxylation reaction. IDH1/2 enzymes catalyzes both the forward and reverse conversion of isocitrate to αKG. Mutations in IDH1/2 cause elevated levels of R-2HG (D-2HG), which is a pro-oncogenic factor. αKG, α-ketoglutarate; ICT, isocitrate; CT, citrate; CS, citrate synthase; FH, fumarate hydratase; FAs, fatty acids. Adapted from Al-Khallaf H. (2017) [26].