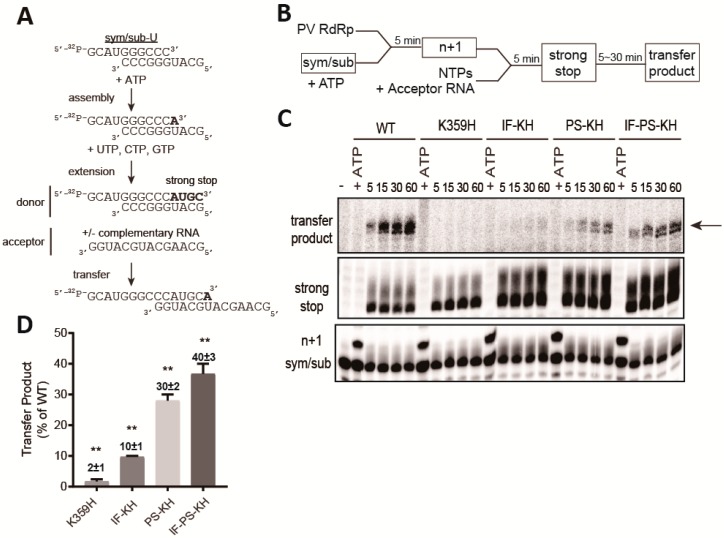
Figure 5.
Properties of the RdRp required for copy-choice recombination in vitro are separable from those required for forced-copy-choice recombination in vitro. (A) The heteropolymeric, symmetrical, primed-template substrate (sym/sub) has been used to establish an assay for forced-copy-choice recombination in vitro [23,45]. RdRp assembles on sym/sub. ATP is added and incorporated to yield a stable elongation complex. It is this elongation complex that is monitored for extension and transfer. Transfer is strictly dependent on the presence of an acceptor RNA with complementarity to the 3′-end of donor RNA. (B) Schematic of the experimental design is indicated. Products in boxes are those observed and monitored by denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. (C) Reaction products were resolved by electrophoresis and detected by phosphorimaging. The only regions of the gel with bands are shown; these correspond to the sym/sub primer, one-nucleotide-extended primer (n+1), four-nucleotides-extended product (strong stop) and non-templated addition of nucleotides to that product, and the transfer product. (D) Transfer products were quantified and are expressed as a percentage relative to the value observed for WT (The concentrations (µM) of n+1 formed for WT, K359H, IF-KH, PS-KH and IF-PS-KH are 0.22, 0.22, 0.32, 0.36, and 0.37, respectively. The concentrations (µM) of transfer product for WT, K359H, IF-KH, PS-KH, and IF-PS-KH are 0.011, 0.00011, 0.0016, 0.0072, and 0.01, respectively. Overall, transfer efficiency ranges from 1% to 5%. Error bars represent SEM (n = 3). Statistical analyses were performed using unpaired, two-tailed t-test (** significance level p = 0.0001).