Figure 1.
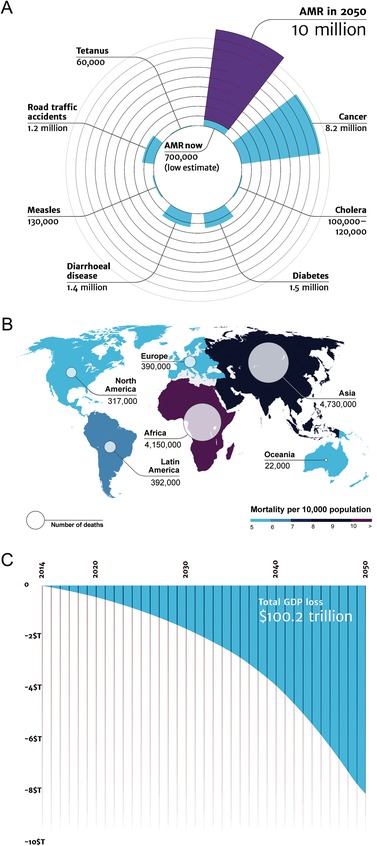
Impact of antimicrobial resistance. Two teams from Europe modeled the increase in the rates of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) based on the information available in 2014, each using their own methodology, to understand the impact of AMR would have on the world population and its economic output. A) Deaths attributable to AMR every year compared to other major causes of death. The estimated number of AMR will increase to 10 million by 2050, approaching the total number of deaths caused by all diseases today. B) Deaths attributable to AMR in different parts of the world by 2050. There is a tendency for reduced mortality continents with better economic conditions and more stringent antibiotic management. C) The impact of AMR on the world's economy between 2014 and 2050 (in trillions of US dollars) predicts an exponentially loss in gross domestic product (GDP) attributable to combating AMR. Reproduced under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International Public License.8 Copyright 2016, Review on Antimicrobial Resistance.
