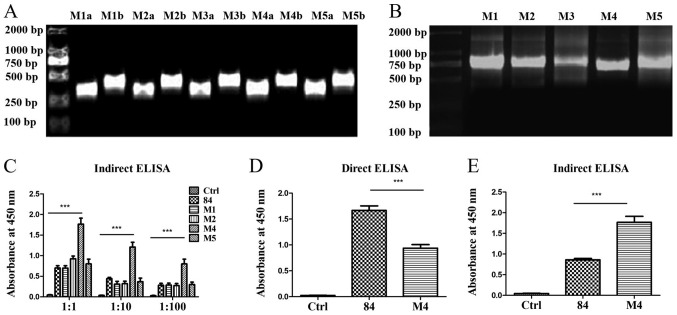
Figure 4.
Amplification of mutated scFv by PCR and detection of scFvs binding to TSLP by ELISA. (A) PCR amplification of (a) the 5′ end of the coding sequences and (b) the 3′ end of the coding sequences containing the mutated amino acids of the scFv 84 separately. (B) Joining of the 5′ end of the coding sequences and 3′ end of the coding sequences containing the mutated amino acids using overlap extension PCR. (C) Indirect ELISA was used to detect the binding of scFvs with TSLP by coating the wells of ELISA plates with the TSLP antigen. 84 refers to the sequence prior to mutation, M1, M2, M4 and M5 refer to sequences following mutation. (D) ELISA detection of the expression levels of pre-mutated scFv-84 and mutated scFv-M4. (E) Indirect ELISA for the detection of the binding of pre-mutated scFv-84 and mutated scFv-M4 to TSLP. ***P<0.001. scFv, single-chain antibody variable fragment; TSLP, thymic stromal lymphopoietin.