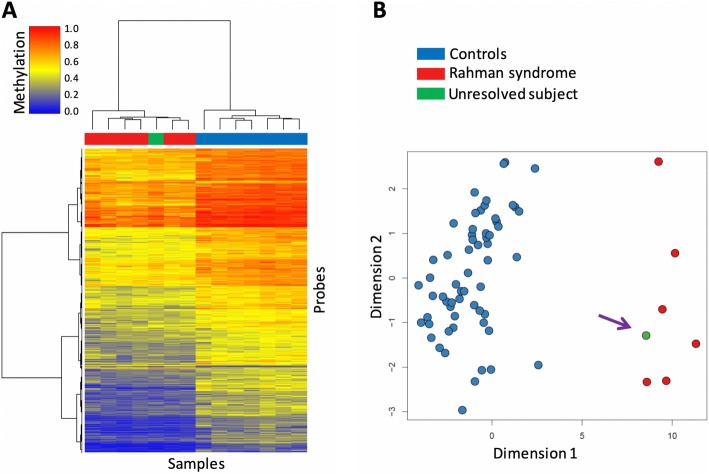
Fig. 1.
A specific episignature characterizes individuals affected by Rahman syndrome. a The DNA methylation profile of a set of seven healthy controls and seven affected individuals (including six patients with previously confirmed molecular diagnosis of Rahman syndrome and one previously undiagnosed subject) is visualized using hierarchical clustering analysis. Rows represent all of the differentially methylated CpG sites (~ 9000) and columns indicate the samples. The color scheme of the top panel is indicative of the class. Red, Rahman syndrome; Blue, controls; Green, undiagnosed individual. The heatmap color scale from blue to red represents the range of the methylation levels (beta values) between 0 and 1. Clustering is performed using Ward’s method on Euclidean distance. b The first two dimensions from multidimensional scaling (MDS) of the DNA methylation levels at CpG sites differentially methylated in Rahman syndrome (RMNS) completely separate all of the patients (red) and controls (blue) from each other. Addition of a subject later identified from a cohort of unresolved DD/ID patients (green—indicated with an arrow) to this analysis, clusters the proband with other RMNS. MDS was calculated by scaling of the pair-wise Euclidean distances between the samples