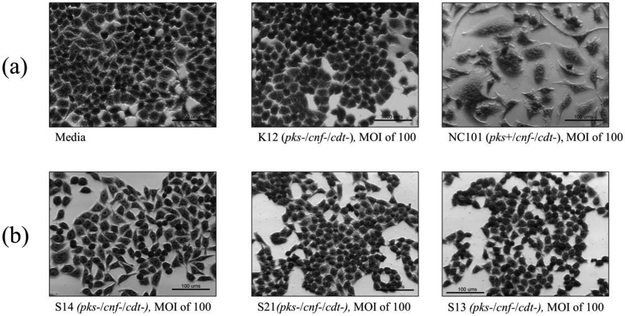
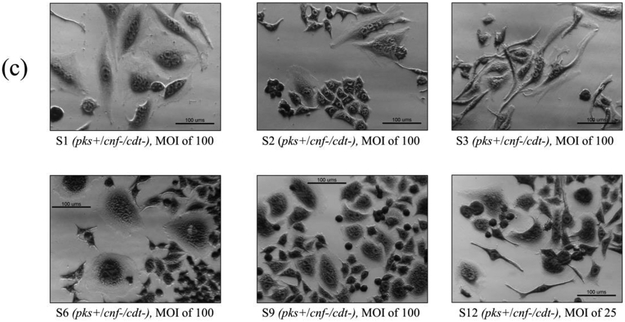
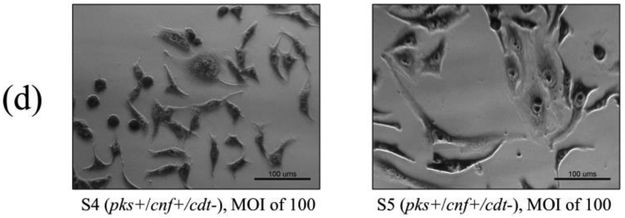
Figure 3.
In vitro infection of HeLa cells with live E. coli isolates, including controls (a), pks−/cnf−/cdt− isolates (b), pks+/cnf−/cdt− isolates (c), and pks+/cnf+/cdt− isolates (d). HeLa cells were treated with E. coli at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) 25 or 100 for 4 h, followed by a 72 h incubation in gentamicin-containing media. Cells infected with the 12 isolates encoding pks (seen in c and d) displayed megalocytosis (enlargement of the cell body and nucleus) similar to the pks positive control. No cytotoxicity was observed for cells treated with K12, media, or representative E. coli isolates negative for pks, cnf and cdt. K12 was used as a non-pathogenic E. coli control. NC101 was used as a pks positive control for colibactin-induced cytotoxicity. Media was used as a negative control for uninfected cells.