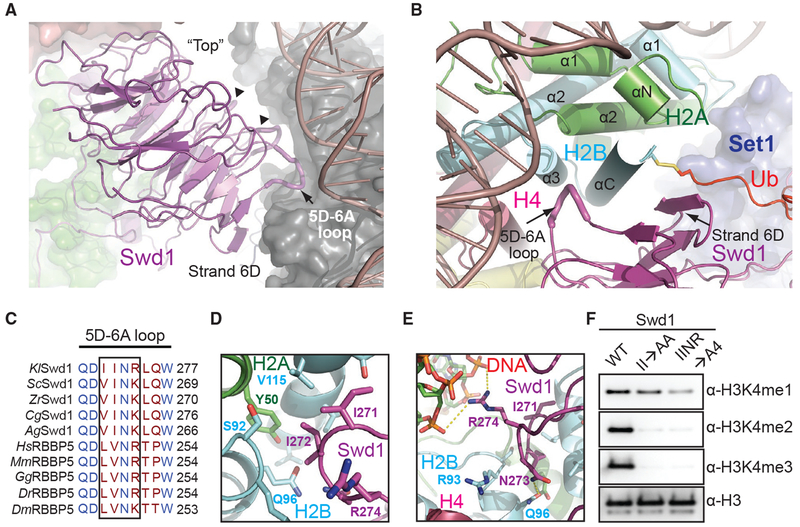
Figure 4. Swd1 Is a Histone-Binding Protein.
(A) Side view of Swd1 (magenta, cartoon) positioned over the histone surface (dark gray, surface). The “top” face of the WD40 is pointed toward the nucleosome, while the “bottom” is facing COMPASS, interacting with Swd3 (green, surface). The top surface loops interacting with the histone surface are shown in tube representation. The 5D-6A loop (tube form) and strand D from blade 6 are labeled. The two loops interacting with H3 and H4 are indicated by triangles.
(B) Top-down view, looking down the C-terminal H2B helix (cyan). Swd1 (magenta) wraps around this helix using the 5D-6A loop (tube form) and strand 6D. Set1 is shown in blue surface representation. H2A and H4 are shown in green and deep red, respectively, in cartoon form. The C-terminal tail of Ub (red) is fused to H2B via a disulfide linkage.
(C) Local structure-based sequence alignment of the 5D-6A loop across K. lactis (Kl), S. cerevisiae (Sc), Z. rouxii (Zr), C. glabrata (Cg), A. gossypii (Ag), H. sapiens (Hs), M. muscuius (Mm), G. gallus (Gg), D. rerio (Dr), and D. meianogaster (Dm) orthologs. Straight line denotes an element with no secondary structure. The four-residue segment that inserts itself into the H2A-H2B three-helix cleft is boxed.
(D) Close-up view centered on the two conserved hydrophobic residues in the 5D-6A loop (magenta) at the three-helix juncture (H2B in cyan, H2A in green).
(E) Close-up view centered on the two polar residues in the 5D-6A loop (magenta). Asn273 forms a hydrogen bond with H2B Gln96 (cyan), while Arg274 interacts with the phosphate backbone of nucleosomal DNA (red, sticks). Polar and salt bridge interactions are shown as dotted yellow lines.
(F) H3K4 methyltransferase activity of the COMPASS CM assembled with Swd1 5D-6A loop mutants against nucleosomal substrates. A double mutant of two hydrophobic residues (II→AA) reduces methyltransferase activity to monomethylation. A quadruple mutant (IINR→A4) nearly renders the CM inactive.