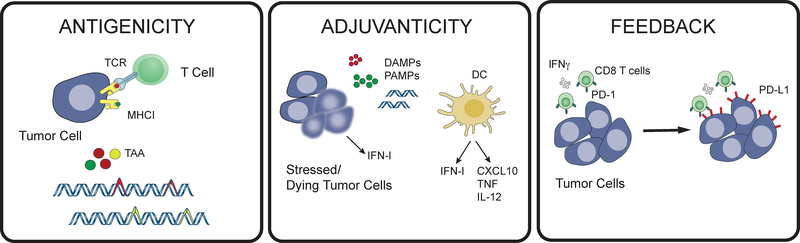
Figure 1: Three discriminatory functions of the immune system, antigenicity, adjuvanticity, and feedback regulation, are critical for promoting anti-tumor immunity.
T cells recognize tumor associated antigens (TAA), which can be generated by mutations in tumor cells, when presented in the context of class I MHC. The presence of non-self antigens must be accompanied by danger signaling to activate the innate immune system, promote dendritic cell (DC) maturation, and T cell activation. Normal homeostatic feedback mechanisms then curb the immune response to limit immunopathology after clearance of pathogens.