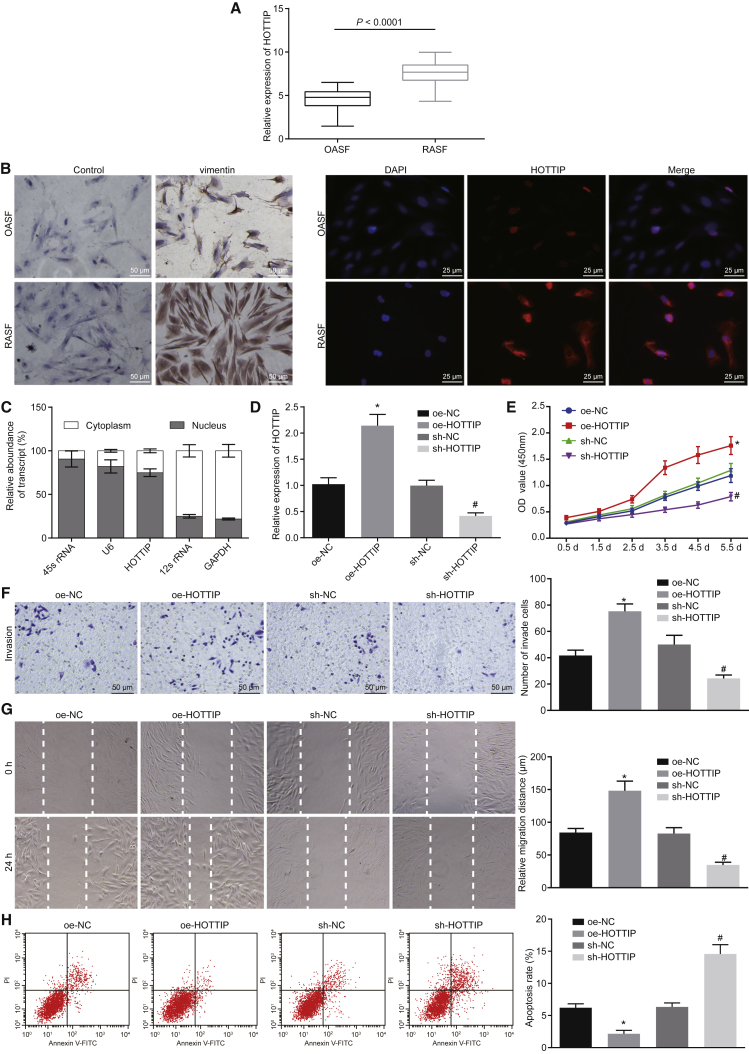
Figure 1.
Downregulation of HOTTIP Suppressed the Proliferation and Enhanced the Apoptosis of RASFs
(A) The HOTTIP expression in RASFs and OASFs determined by qRT-PCR. (B) Immunocytochemical staining of vimentin expression in the isolated of RASFs and OASFs (×200) and subcellular localization of HOTTIP in RASFs and OASFs by FISH (×400). (C) Subcellular localization of HOTTIP in RASFs determined by qRT-PCR after nuclear and cytoplasmic fractionation. (D) The infection efficiency of lentivirus expressing overexpressed (oe)-HOTTIP or short hairpin RNA (sh)-HOTTIP in RASFs was determined by qRT-PCR. GAPDH was used as an internal control. (E–H) Cell proliferation, invasion, migration (×200), and apoptosis were assessed in RASFs upon overexpression or silencing of HOTTIP determined by WST-1 assay (E), Transwell assay (F), scratch test (G), and flow cytometry (H), respectively. *p < 0.05 compared with RASFs infected with lentivirus expressing oe-negative control (NC); #p < 0.05 compared with RASFs infected with lentivirus expressing sh-NC. The results were expressed as mean ± SD. Comparisons between two groups were conducted by means of t test. The data at different time points (E) were analyzed by repeated-measurement ANOVA. Comparisons among multiple groups were analyzed by one-way ANOVA. The experiment was repeated three times.