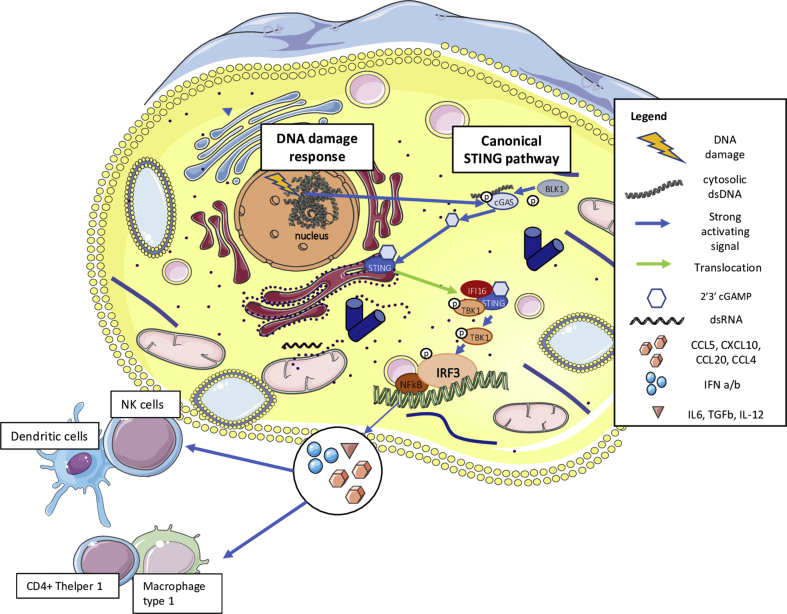
Figure 2.
Canonical STING pathway activation. Elevated levels of basal DNA damage results in the increase of cytosolic DNA (cDNA) which induces an activation of cGAS and, consequently, the translocation of STING from the endoplasmic reticulum to the nucleus. There, STING pathway leads to the transcription of several IFN type I–related genes by IRF3 activation, thus inducing the production of IFN type I and chemoattractive cytokines, that is, chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 10 (CXCL10) and chemokine (C–C motif) ligand 5 (CCL5). This leads to NK cell, M1-like macrophage and both T- and B-lymphocyte recruitment in an Ag-independent manner. STING = stimulator of interferon genes; cGAS = cyclic GMP-AMP synthase; IFN = interferon.