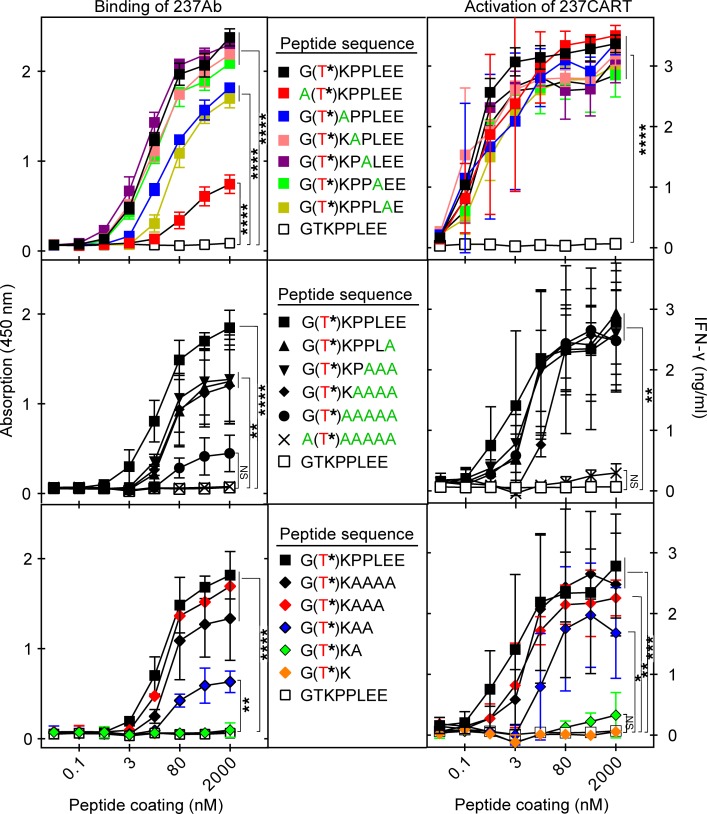
Figure 5. Recognition by 237CART cells is more permissive to amino acid residue substitutions and truncations of the Tn-glycopeptide epitope than that by 237Ab.
Biotinylated peptides immobilized on a streptavidin-coated plate surface at the indicated coating concentrations were tested for binding by 237Ab measured by light absorption at 450 nm, or stimulation of 237CART cells measured by the level of IFN-γ secretion after 24 hours of coincubation. The Tn-glycosylated Thr77 of murine PDPN is labeled in red, while the alanine scanning of the original murine PDPN sequence is labeled in green. Top panel: Alanine scanning of the 237Ab-binding epitope, 1 amino acid residue at a time. Middle panel: Alanine scanning of the 237Ab-binding epitope in murine PDPN with an increasing number of residues at a time. Bottom panel: The gradual truncation of the 237Ab-binding epitope from the C-terminus. Mean ± SEM, n = 3 from 3 independent experiments. The significance of the difference between each group at the highest peptide coating concentration in comparison to that of the non–Tn-glycosylated GTKPPLEE group was examined by 1-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test. ns indicates P > 0.05; *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, ****P ≤ 0.0001.