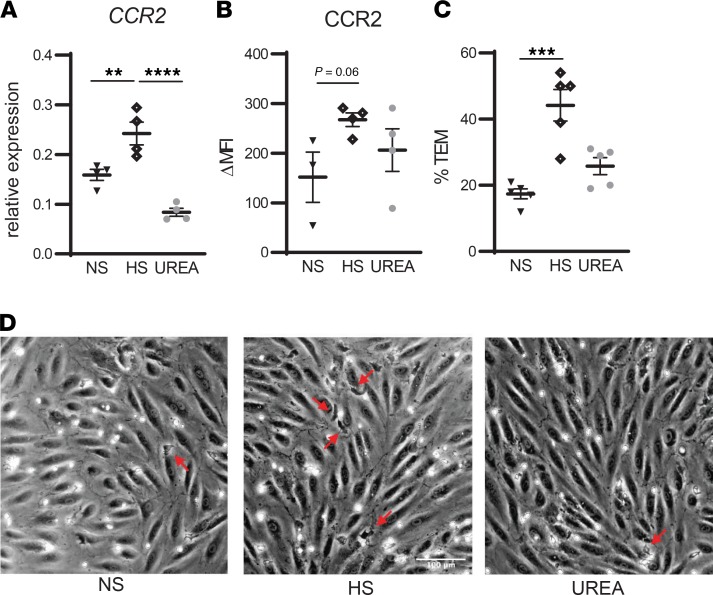
Figure 4. High salt increases CCR2 expression and transendothelial migration of monocytes in vitro.
(A and B) Monocytes of independent healthy donors were stimulated for 24 h in RPMI + 10% FCS + 1% PenStrep in the presence of normal salt (NS), high salt (HS), or 80 mM urea as tonicity control. Then, CCR2 gene expression was assessed with qPCR (A) and protein expression with flow cytometry (B). (C and D) After 24-h incubation in NS, HS, or urea, monocytes were added to the monolayer of cultured human arterial endothelial cells. Transmigrated monocytes (red arrows) were distinguished from adhered monocytes by their transitions from bright to black morphology. NS, ([Na+] = 139 mM); HS, ([Na+] = 179 mM). Values represent mean ± SEM of n = 4 (A and B) and n = 5 (C) healthy donors. Data tested using 1-way ANOVA. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.