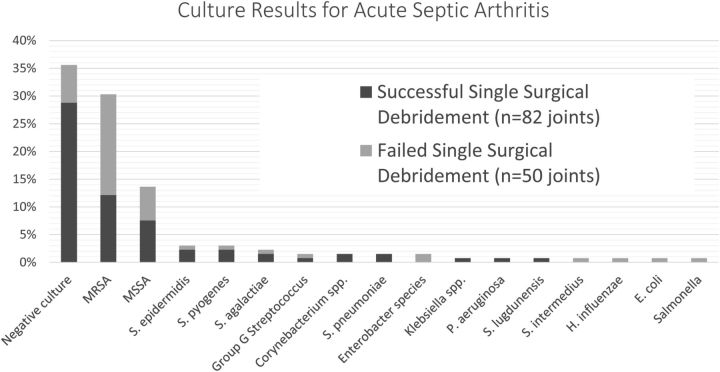
Fig. 1.
The final culture results for adults with acute septic arthritis. Negative or sterile culture results were the most common. Staphylococcus aureus was the most common bacterial isolate identified (45%) and more common in joints that failed a single surgical debridement (66% compared with 33%; p < 0.001). No other significant differences were observed between the two groups on analysis of culture data (p > 0.05). MRSA = methicillin-resistant S. aureus, MSSA = methicillin-sensitive S. aureus, S. epidermidis = Staphylococcus epidermidis, S. pyogenes = Streptococcus pyogenes, S. agalactiae = Streptococcus agalactiae, S. pneumoniae = Streptococcus pneumoniae, P. aeruginosa = Pseudomonas aeruginosa, S. lugdunensis = Staphylococcus lugdunensis, S. intermedius = Streptococcus intermedius, H. influenzae = Haemophilus influenzae, and E. coli = Escherichia coli.