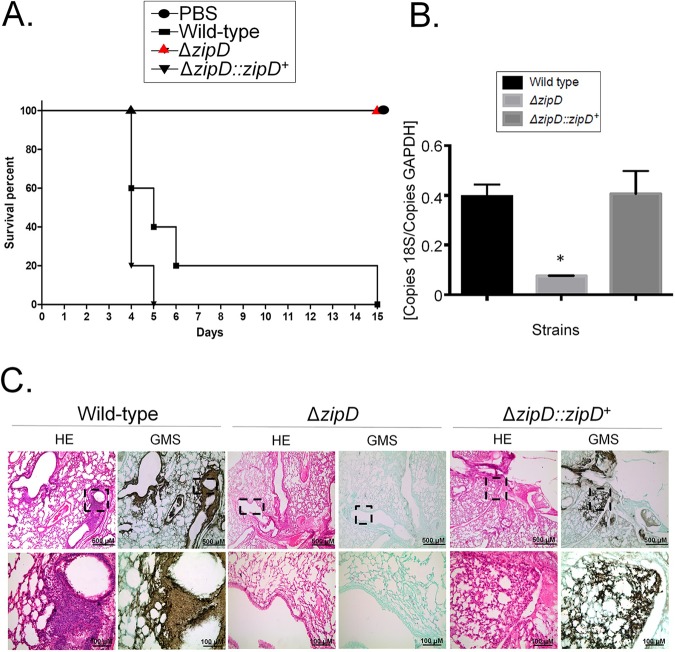
Fig 7. ΔzipD has highly attenuated virulence in neutropenic mice.
(A) Comparative analysis of wild-type, ΔzipD, and ΔzipD::zipD+ strains in a neutropenic murine model of pulmonary aspergillosis. Mice in groups of 10 per strain were infected intranasally with a 20 μl suspension of conidia at a dose of 105. PBS = phosphate Buffer Saline; *, p<0.001 comparison between the wild-type and ΔzipD mutant, for both Log−rank, Mantel−Cox and Gehan−Breslow−Wilcoxon tests. (B) Fungal burden was determined 48 hours post-infection by real-time qPCR based on 18S rRNA gene of A. fumigatus and an intronic region of the mouse GAPDH gene. Fungal and mouse DNA quantities were obtained from the Ct values from an appropriate standard curve. Fungal burden was determined through the ratio between ng of fungal DNA and mg of mouse DNA. The results are the means (± standard deviation) of five lungs for each treatment. Statistical analysis was performed by using t-test (*, p < 0.01). (C) Histopathology of mice infected with A. fumigatus wild-type, ΔzipD and ΔzipD::zipD+ mutant strains. GMS (Grocott's Methenamine Silver) and HE (Hematoxylin and Eosin) staining of lung sections of representative of infections. The hatched area from the top row is amplified in the lower row. Bars, 100 and 500 μm.