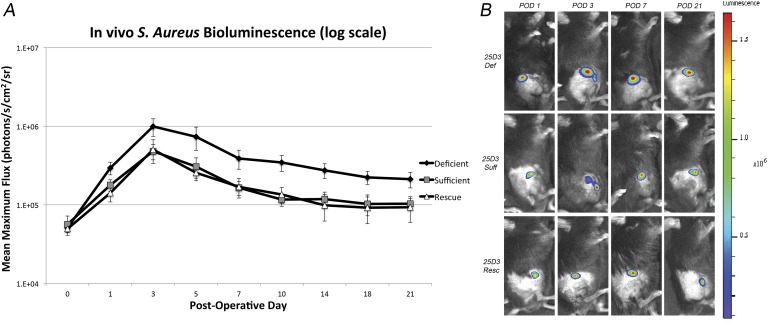
Fig. 2.
Figs. 2-A and 2-B Measurement of bacterial burden in vivo using live-animal bioluminescence in 25D3-deficient (def), sufficient (suff), and rescued (resc) mice. A stainless steel implant was inserted into the right knee joint of the mice (n = 20 per group), and the joint space was inoculated with Xen36 Staphylococcus aureus (1 × 103 colony-forming units) possessing the bioluminescent construct in a stable plasmid. Fig. 2-A Bacterial counts as measured by S. aureus bioluminescence in vivo (mean maximum flux and standard error of the mean [logarithmic scale]). Fig. 2-B Representative in vivo S. aureus bioluminescence on a color scale overlaid on a grayscale image of the mouse. POD = postoperative day.