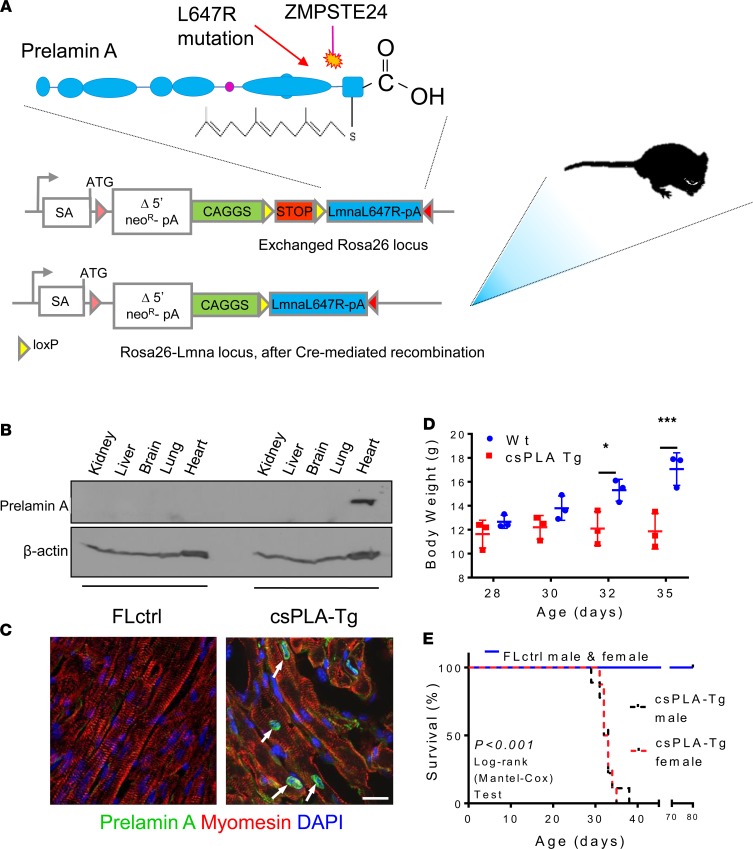
Figure 2. Targeted transgenesis of prelamin A led to nuclear accumulation in CMs and resulted in premature death in mice.
(A) Schematic representation showing the site of prelamin A (LMNA-L647R) cDNA insertion and the modifications required for conditional expression. SA, splice acceptor site; neoR, neomycin resistance; pA, polyadenylation signal. (B) Western blotting for prelamin A showing expression was restricted to heart tissue. (C) Confocal micrographs of myocardium stained for prelamin A showing nuclear rim localization in csPLA-Tg hearts. Scale bar: 10 μm. Arrows indicate prelamin A expressing nuclei. (C) Growth curves showing that csPLA-Tg mice stop growing after 30 days. n = 3 males/group. Two-way ANOVA with repeated measures with Sidak’s post hoc test for multiple comparisons was performed. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001. (D) Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showing that csPLA-Tg male and female mice exhibited attenuated survival compared with FLctrl counterparts. n = 7 FLctrl males, 8 FLctrl females, 9 csPLA-Tg males, 8 csPLA-Tg females. Log-rank Mantel-Cox test was performed. P < 0.0001.