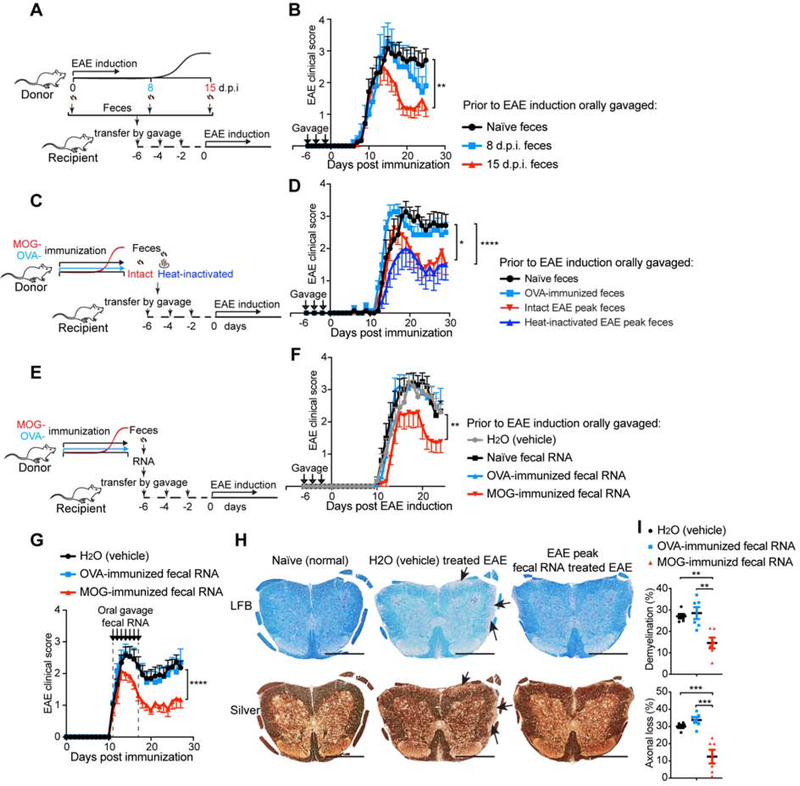
Figure 2. Both Fecal Transfer and Fecal RNA Transfer from Peak EAE Donor Ameliorate EAE in Recipients.
(A-B) The effect of transfer of feces from different stages of EAE on EAE in recipient mice. (A) Schematic design. Donor mice were immunized with MOG/CFA to induce EAE. Feces were collected at day 0 (naïve), day 8 post immunization (8 d.p.i., prior to symptom onset), and 15 d.p.i. (peak) and orally gavaged to recipient mice 6 days-, 4 days- and 2 days- prior to the induction of EAE in the recipients. (B) Clinical scores of EAE in recipient mice. 0 d.p.i. n=12, 8 d.p.i. n=5, and 15 d.p.i. n=12. Error bars denote mean ± SEM; Friedman test based on scores from the first onset of EAE (7 d.p.i.) until the end of experiment followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison test as compared with group of naïve feces recipients. (C-D), Analysis of the role of live bacteria in the EAE fecal transfer. (C) Experimental scheme. Donor mice were immunized with MOG or OVA. Feces were collected at 15 d.p.i. (EAE peak), heat-inactivated or kept intact, and orally gavaged to recipient mice 6 days-, 4 days- and 2 days- prior to EAE induction in the recipients. (D) Clinical scores of EAE in recipients. n=7 each group; Error bars denote mean ± SEM; Friedman test based on scores from the onset of EAE (11 d.p.i.) until the end of experiment followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison test as compared with the naïve feces-gavaged mice. (E-F) Effect of oral administration of MOG-induced EAE peak fecal RNA on EAE. (E) Experimental scheme. Donor mice were immunized with MOG or OVA. Feces were collected at 15 d.p.i. when the MOG-immunized mice were at peak of EAE. Fecal RNA was isolated from donor feces and orally gavaged 6 days-, 4 days- and 2 days- prior to induction of EAE in the recipients. (F) Clinical scores of EAE in the recipients. n=10 each group; Error bars denote mean ± SEM; Friedman test based on scores from the onset of EAE (11 d.p.i.) until the end of experiment followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison test as compared with the H2O-gavaged group. (G-I) Therapeutic effect of oral administration of EAE peak fecal RNA on established EAE. Fecal RNA isolated from EAE peak or OVA-immunized mice was orally gavaged to EAE recipients at the dose of 10 μg RNA /mouse daily for 7 consecutive days starting when recipients had a disease score = 1. (G) Clinical scores of EAE in the recipient mice, representative data of three independent experiments, H2O (vehicle) n=13, OVA-induced n=12, MOG-induced n=13; Error bars denote mean ± SEM; Friedman test based on scores from the onset of EAE (11 d.p.i.) until the end of experiment followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison test as compared with the H2O-gavaged group. (H) Histopathological evaluation of demyelination with Luxol Fast Blue (LFB) and axonal loss with Bielschowsky’s silver (Silver) staining of representative spinal cord sections from naïve mice and EAE mice treated with feces from H2O (vehicle) or EAE peak EAE feces. Arrows denote demyelination (LFB) and axonal lost (Silver) in H2O (vehicle) treated EAE, scale bars, 500 μm. (I) Quantification of demyelination and axonal loss based on LFB and Silver staining for individual mice. Representative data of three independent experiments with n=6 mice/group, Error bars denote mean ± SEM, one-way ANOVA Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. All panels: n.s.= not significant, * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001, **** P<0.0001.