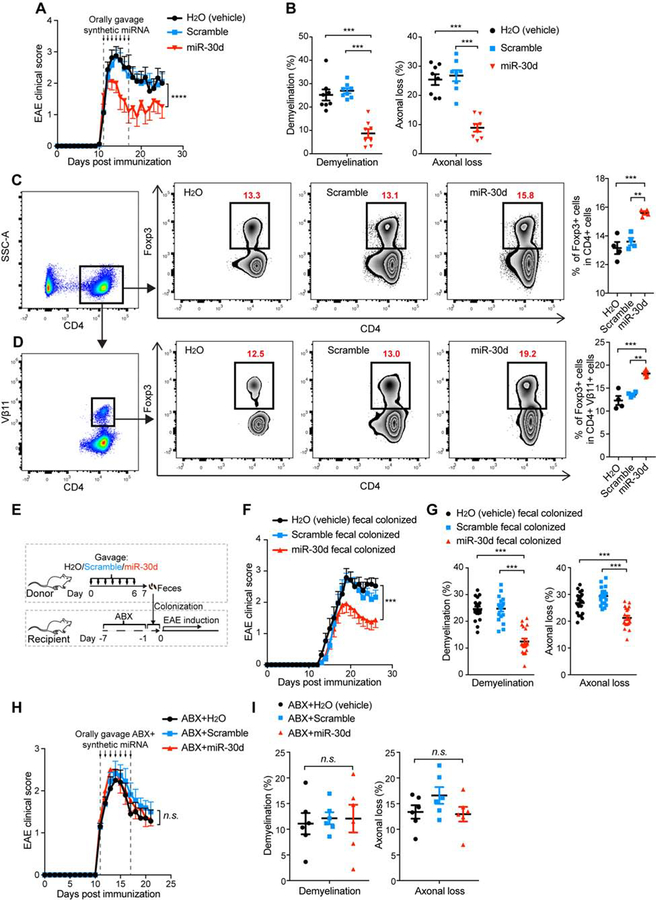
Figure 4. Oral Administration of Synthetic miR-30d Ameliorates EAE in a Recipient Gut Microbiome-dependent Manner.
(A-B) synthetic miR-30d or scramble control was orally gavaged to EAE recipients starting at disease onset (day 11, disease score=1) daily at a dose of 250 pmol for 7 consecutive days. (A) Clinical scores of EAE in the recipient mice. Representative data of two independent experiments; H2O(vehicle) n=8, scrambled miR-30d n=13, miR-30d n=11, Error bars denote mean ± SEM, Friedman test based on scores after the beginning of treatment (12 d.p.i) until the end of experiment followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison test as compared with the H2O-gavaged group. (B) Quantification of demyelination and axonal loss for individual mice. Data combined from two independent experiments with n=8 mice/group; Error bars denote mean ± SEM, one-way ANOVA Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. (C-D) Mice were immunized with MOG and orally administered synthetic miR-30d or scramble control daily at a dose of 1000 pmol for 7 consecutive days. Foxp3+ T cells in the total CD4+ T cell population (C) and in the Vβ11+ CD4+ T cell population (D) in the spleen were analyzed by FACS. Left panel: Representative FACS plots of Foxp3+ CD4+ T cells; Right panel: % of CD4+ Foxp3+ T cells in individual animals (n=4 per group). Error bars denote mean ± SEM; one-way ANOVA Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. (E-G) Effect on EAE of transfer of fecal microbiome from synthetic miR-30d treated mice. Donor mice were immunized with MOG and orally treated with H2O (vehicle), scrambled miR-30d, or miR-30d for 7 consecutive days. Feces were collected and used to colonize mice that were pre-treated with antibiotics (ABX) for 7 days prior to colonization. Recipient mice were then induced for EAE. (E) Experimental scheme. (F) Clinical scores of EAE in the recipient mice. Combined data of two experiments with H2O (vehicle) n=19, scramble n=21, miR-30d n=24; Error bars denote mean ± SEM; Friedman test based on scores from the onset of disease (11 d.p.i) until the end of experiment with Dunn’s multiple comparisons as compared with the H2O-treated donor feces-colonized group. (G) Quantification of demyelination and axonal loss. Values for individual mice are shown, combined from 2 independent experiments with H2O (vehicle) n=19, scramble n=19, miR-30d n=20; Error bars denote mean ± SEM, one-way ANOVA Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. (H-I) Antibiotics abrogated therapeutic effect of oral miR-30d on EAE. Synthetic miR-30d, scramble control, or H2O (vehicle) was orally gavaged to EAE recipients starting at the onset of disease (day 11, disease score =1) at a dose of 250 pmol daily for 7 consecutive days. Mice were simultaneously gavaged with an antibiotics mixture (ABX). (H) Clinical scores of EAE, Combined data from two independent experiments, H2O (vehicle) n=10, Scramble n=11, miR-30d n=11, Error bars denote mean ± SEM, Friedman test based on scores from the start of the treatment (11 d.p.i) until the end of experiment followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison test as compared with the ABX+H2O-gavaged group. (I) Quantification of demyelination and axonal loss for individual mice from two independent experiments (n=6 mice/group); Error bars denote mean ± SEM, one-way ANOVA Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. All panels: n.s.= not significant, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001, **** P<0.0001.