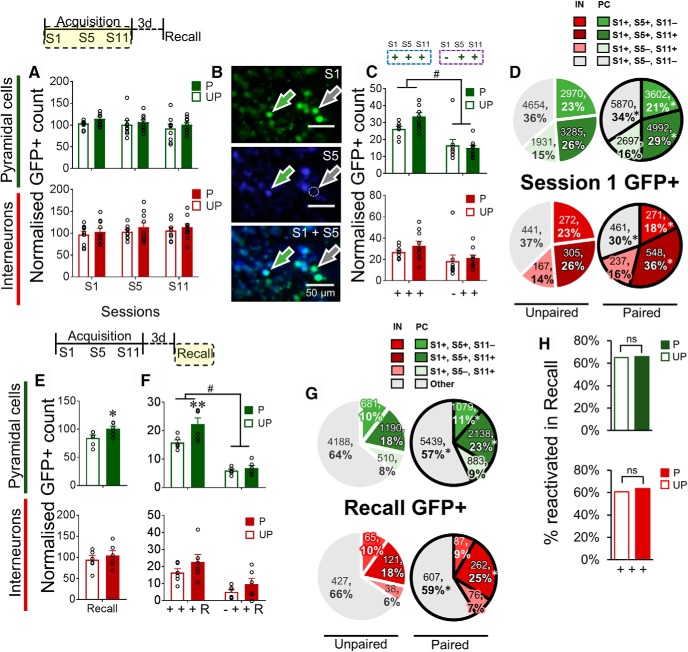
Figure 4.
Conditioning and memory recall recruit a stable pyramidal cell (PC) ensemble from the initial acquisition session. A, Normalized GFP+ counts of PCs (green) and interneurons (IN) (red) during acquisition sessions. B, Representative image of longitudinal GFP imaging (S1 and S5). Green arrow indicates S1+|S5+ neurons. Gray arrow indicates S1+|S5− neurons. C, Normalized GFP+ counts of PCs and INs with an S1 (+ + +) or no S1 (− + +) activation history. D, Distribution of GFP+ PCs and INs activated during S1 classified according to their subsequent reactivation patterns (S1+|S5+,S11+; S1+|S5+, S11−; S1+|S5−, S11+; S1+|S5−,S11−) for Paired and Unpaired mice. E, Normalized GFP+ counts of PCs and INs following the test for memory recall. F, Normalized GFP+ counts of PCs and INs recruited during the test for recall that had been persistently activated during training, as a function of their S1 activation history (+ + + R or − + + R). G, Distribution of GFP+ PCs and INs activated during the test for recall, classified according to their activation patterns from S1 onwards in Paired and Unpaired mice. Other, Neurons recruited during recall that did not demonstrate activation histories of interest (e.g., S1−|S5−, S11+). H, Proportion of S1+|S5+ S11+ PCs and INs that were reactivated in Recall for Paired and Unpaired mice. Data on bar graphs are mean ± SEM. Normalization of GFP+ counts was performed using the average number of GFP+ neurons in HC (number of GFP+ cells/average number of GFP+ in HC) ×100). Interaction effect: #p < 0.05. Post hoc analysis: **p < 0.01. Paired (P), n = 10; Unpaired (UP), n = 9 for acquisition; Paired (P), n = 6; Unpaired (UP), n = 6 for Recall.