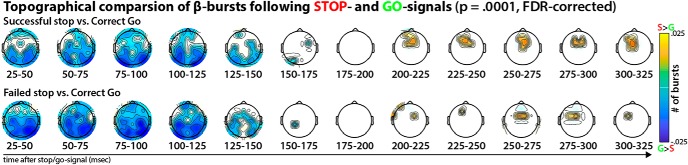
Figure 3.
Statistical comparison of β-burst topographies following Stop- and Go-signals, separately for successful (top) and failed (bottom) Stop-trials. Thresholded for significance at p < 0.0001, FDR-corrected for multiple comparisons across channels and time windows. It is evident that while movement initiation (Go-trials) was accompanied by a significantly relative increase in β-burst count at bilateral sensorimotor sites until ∼175 ms after the Go-signal, movement cancellation was accompanied by significant relative increase of β-burst rates at fronto-central electrodes, starting at ∼200 ms after the Stop-signal.