Figure 1.
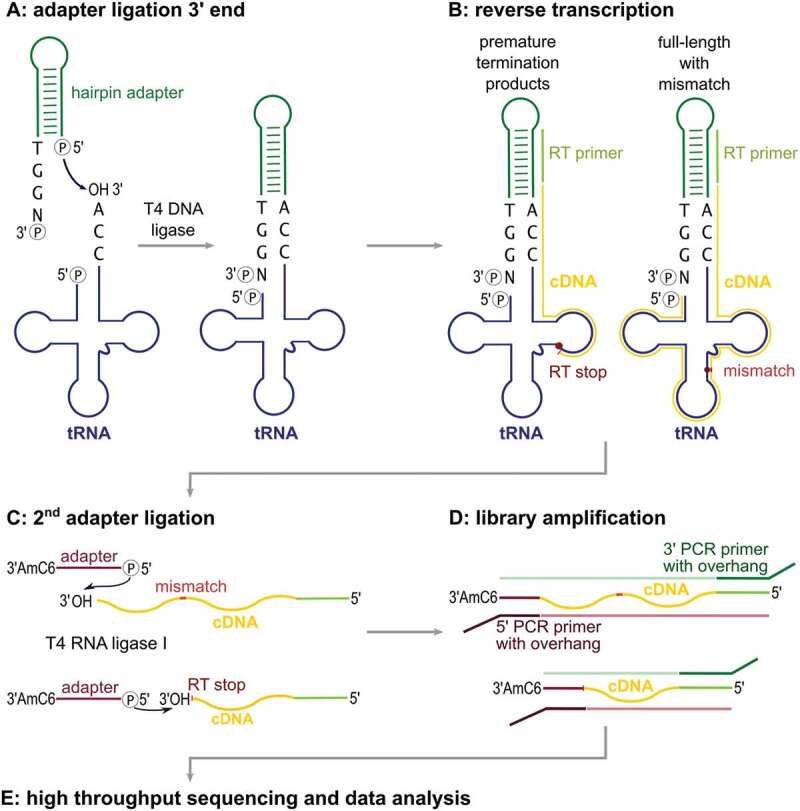
Schematic workflow of the LOTTE-seq procedure. (A) A DNA hairpin-oligonucleotide (green) with a 3ʹ-TGGN overhang hybridizes to the tRNA 3ʹ-CCA end (tRNA in blue). T4 DNA ligase fuses the 3ʹ-end of the CCA terminus to the phosphorylated 5ʹ end of the adapter. (B) The tRNA is reverse transcribed with parts of the hairpin oligonucleotide serving as primer binding site. Secondary structure and modified bases can lead to premature RT stops and partial cDNA (yellow). (C) Using T4 RNA ligase I, a 5ʹ-phosphorylated and 3ʹ-blocked second adapter (red) is fused to the 3ʹ-end of the cDNA, leading to the generation of cDNA product with adapters on both sides (red and green). (D) This product is PCR-amplified with indexed primers binding to the adapter overhang sequences. (E) The cDNA library consisting of full-length as well as prematurely terminated tRNA sequences is analysed by high-throughput sequencing.
