Figure 1.
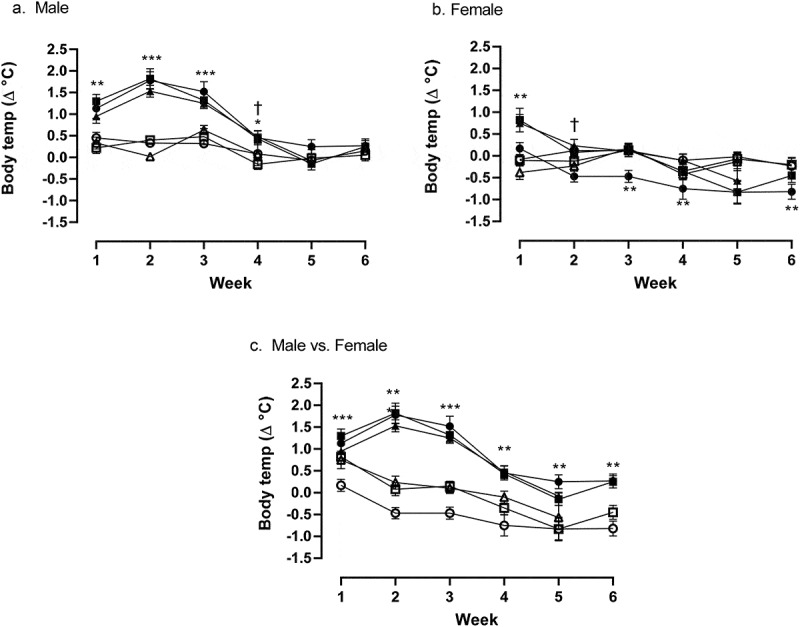
(a) Weekly comparison of ∆°C from baseline temperature in male treatment group at 30 (●), 60 (■), and 90-min (▲) post treatment vs male saline controls at 30 (○), 60 (□), and 90-min (△) time points. Significance of hyperthermic response is denoted by asterisks; * = p < 0.05, ** = p < 0.01, *** = p < 0.001, while significant tolerance effects are denoted by †. (b) Weekly comparison of ∆°C from baseline temperature in female treatment group at 30 (●), 60 (■), and 90-min (▲) post treatment vs female saline controls at 30 (○), 60 (□), and 90-min (△) time points. Significance of hyperthermic response is denoted by asterisks; * = p < 0.05, ** = p < 0.01, *** = p < 0.001, while significant tolerance effects are denoted by †. Significant hypothermic effect is denoted by cent sign. (c) Weekly comparison of ∆°C from baseline temperature in male treatment group at 30 (●), 60 (■), and 90-min (▲) post treatment vs female treatment group at 30 (○), 60 (□), and 90-min (△) time points. Significance of hyperthermic response is denoted by asterisks; * = p < 0.05, ** = p < 0.01 =, *** = p < 0.001.
