Fig. 2. MRN, DNA-PK, and CtIP promote dsDNA end resection.
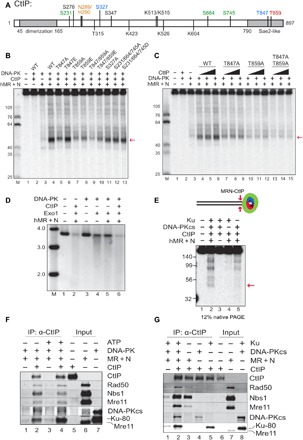
(A) A linear map of CtIP indicating a subset of known phosphorylated residues as well as residues important for DNA binding and catalytic activity as discussed in the text (orange, sites required for nuclease activity; green, ATM-dependent phosphorylation sites; blue, CDK-dependent phosphorylation sites; red, ATR/ATM-dependent phosphorylation site). (B) Nuclease assays were performed with MRN (12.5 nM), CtIP (40 nM), Ku (10 nM), DNA-PKcs (10 nM), and NU7441 as in Fig. 1A but with various mutants of CtIP, as indicated, in the presence of both magnesium and manganese. The red arrow indicates the predominant product formed in the presence of DNA-PKcs. (C) Nuclease assays were performed as in (B) with titrations of CtIP (10, 20, and 40 nM). (D) DNA end resection on a plasmid substrate (3.6 kb) was performed with MRN, CtIP, DNA-PK, and Exo1, as indicated, in the presence of a DNA-PKcs inhibitor. Reaction products were separated in a native agarose gel, which was stained with SYBR Green; molecular weight (MW) ladder migration is shown (kb). (E) dsDNA cleavage products from the MRN nuclease assay with DNA-PK and CtIP were detected on a 12% native polyacrylamide gel. The red arrow indicates the ~45-bp product. (F) Protein-protein interactions between CtIP, MRN, and DNA-PK were measured by IP with anti-CtIP antibody in the presence or absence of ATP followed by Western blotting of bound proteins, as indicated. (G) Interactions between CtIP, MRN, DNA-PKcs, and Ku were measured with CtIP IP as in (F) in the presence of ATP.
