Fig. 2. β-Catenin was induced in the development of obesity in humans and mice.
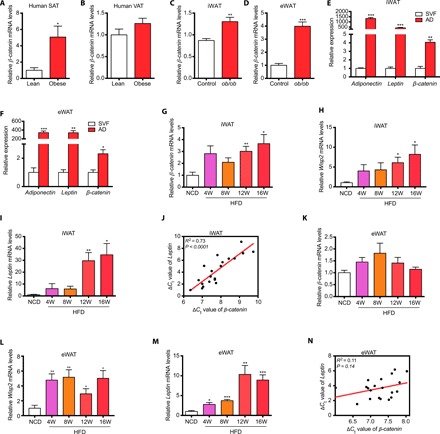
(A) β-catenin expression was significantly higher in subcutaneous adipose tissue of obese subjects than in lean subjects. (B) β-catenin expression was unaltered in visceral adipose tissue of obese subjects compared with that of lean subjects. (For A and B, n = 11 for lean subjects, n = 21 for obese subjects.) (C and D) The expression of β-catenin was higher in inguinal WAT (iWAT) (C) and epididymal WAT (eWAT) (D) of ob/ob mice than in wild-type mice (n = 10 for each group). (E and F) The expression of β-catenin was highly enriched in mature adipocytes than in SVF cells in iWAT (E) and eWAT (F) (n = 3 for each group). Leptin and adiponectin were used as the markers of mature adipocytes. (G to I) β-catenin expression was induced in iWAT during long-term HFD feeding (G) along with high expression of Wisp2 (H) and WAT marker Leptin (I). (J) β-catenin expression was associated with Leptin expression in iWAT. ΔCt values of β-catenin and Leptin were used to examine the association in linear regression analysis. (K to M) β-catenin expression was not significantly induced in eWAT during HFD feeding (K) despite the high expression of Wsip2 (L) and WAT marker Leptin (M). (N) β-catenin expression was not significantly associated with Leptin expression in eWAT. For (G) to (N), n = 4 for each group. AD, adipocyte; SAT, subcutaneous adipose tissue; VAT, visceral adipose tissue; NCD, normal chow diet; HFD, high-fat diet; iWAT, inguinal white adipose tissue; eWAT, epididymal white adipose tissue; SVF, stromal vascular fraction. Data are shown as means ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
