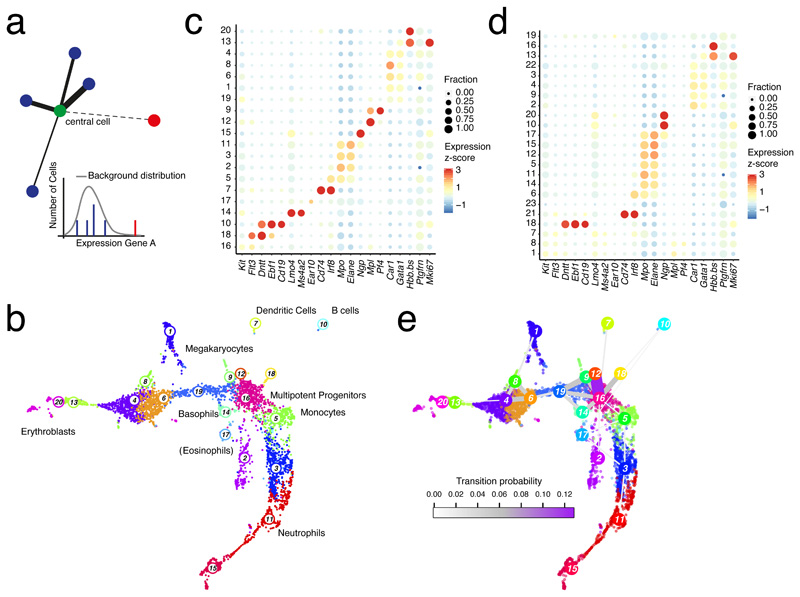
Figure 1. Locally homogenous neighborhoods enable sensitive cell type identification.
a, Strategy for inferring locally homogenous neighborhoods by pruning knn-networks. Links are removed if the transcript levels in a neighboring cell are not explained by a local background model. Thickness of links represents the likelihood of belonging to the same cell state. b, Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection for Dimension Reduction (UMAP) representation21 of mouse hematopoietic progenitor single-cell RNA-seq data10 highlighting clusters inferred by Louvain clustering on the pruned knn-network (k=10 and α=10). Cell type labels are based on marker gene expression. c, Dot plot showing the expression z-score of lineage-specific marker genes across all clusters from (b). The dot size indicates the fraction of cells expressing a gene. d, Dot plot showing expression of lineage-specific marker genes across all clusters inferred by Seurat5,6. See (c) for details. e, UMAP representation with links connecting cluster medoids. The thickness and color of a link indicates the transition probability between the connected clusters. (b-d) Data from n=2 biologically independent experiments.