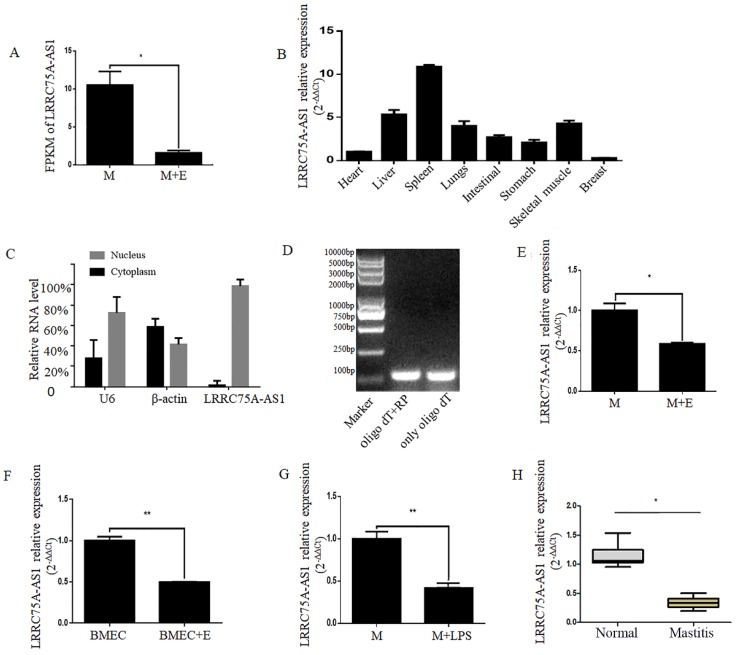
Figure 1.
Validation of LRRC75A-AS1 in cells and tissues by RT-qPCR. (A) FPKM value of LRRC75A-AS1 in MAC-T (M) and MAC-T treated with heat-killed E. coli (M+E) was obtained from RNA sequence data. (B) Expression of LRRC75A-AS1 in eight different tissues was detected by RT-qPCR. (C) LRRC75A-AS1 was detected in nucleus and cytoplasm by RT-qPCR. (D) It was detected that if there is a polyA tail at 3'end of LRRC75A-AS1 by RT-PCR. Both Oligo dT and random primer (RP) were added in the reverse transcription reaction to reverse all transcripts, while Oligo dT only was used to reverse transcript RNA with polyA tail to cDNA for PCR, then the PCR products were separated respectively in lane 1 and lane 2. (E) LRRC75A-AS1 was detected in M and M+E by RT-qPCR. (F) LRRC75A-AS1 was detected in primary bovine mammary epithelium cells (BMECs). (G) LRRC75A-AS1 was detected by RT-qPCR after M was treated with LPS. (H) LRRC75A-AS1 was detected in normal bovine mammary tissues and mastitis tissues. **P<0.01, *P<0.05 vs control.