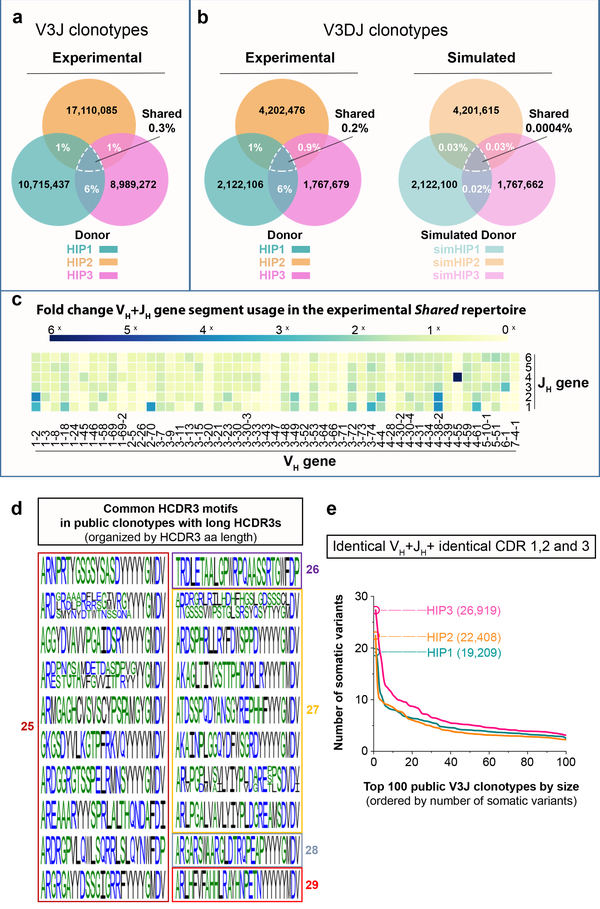
Figure 2. Shared clonotypes between three healthy adult subjects (HIP1, 2 and 3).
(a) Shared V3J clonotypes from sequenced Ig heavy chains. (b) (Left panel) Shared V3DJ clonotypes from sequenced Ig heavy chains with HCDR3 lengths from 3 to 28 amino acids. (Right panel) Shared V3DJ clonotypes from synthetic HIP repertoires with HCDR3 lengths from 3 to 28 amino acids. The percentage overlaps were based on the average of 1,000 comparisons from bootstrap testing involving synthetic HIP repertoires. The average and standard error of the mean (s.e.m.) for the percentage overlaps was 0.03% (5.0 × 10−5) between simHIP1 and simHIP2, 0.03% (4.9 × 10−5) between simHIP1 and simHIP3, and 0.02% (6.0 × 10−5) between simHIP2 and simHIP3. The average and s.e.m. for the percentage overlap between simHIP1 and simHIP2 and simHIP3 was 0.0004% (6.9 × 10−6). The V3DJ overlap count between all three sequenced repertoires (n = 3,641 common clonotypes) ranked highest in the 1,000 comparisons giving a P = 1.0 × 10−4 (see Extended Data Fig. 2e for normalized histogram of common clonotypes between synthetic sets). (c) Fold change in VH+JH usage between Shared HIP1+2+3 (n = 29,062 unique clonotypes) and all HIP subjects (designated: All HIP1+2+3, n = 36,064,712 unique clonotypes). (d) Common motifs in Shared V3J clonotypes with long CDR3s shown as a WebLogo22. (e) Somatic variant count for V3J clonotypes from the Shared HIP1+2+3 collection whose somatic variants had identical CDR1 and CDR2 amino acid sequences plotted in order of decreasing frequency. Numbers in parenthesis denote V3J clonotypes having the largest number of somatic variant counts.