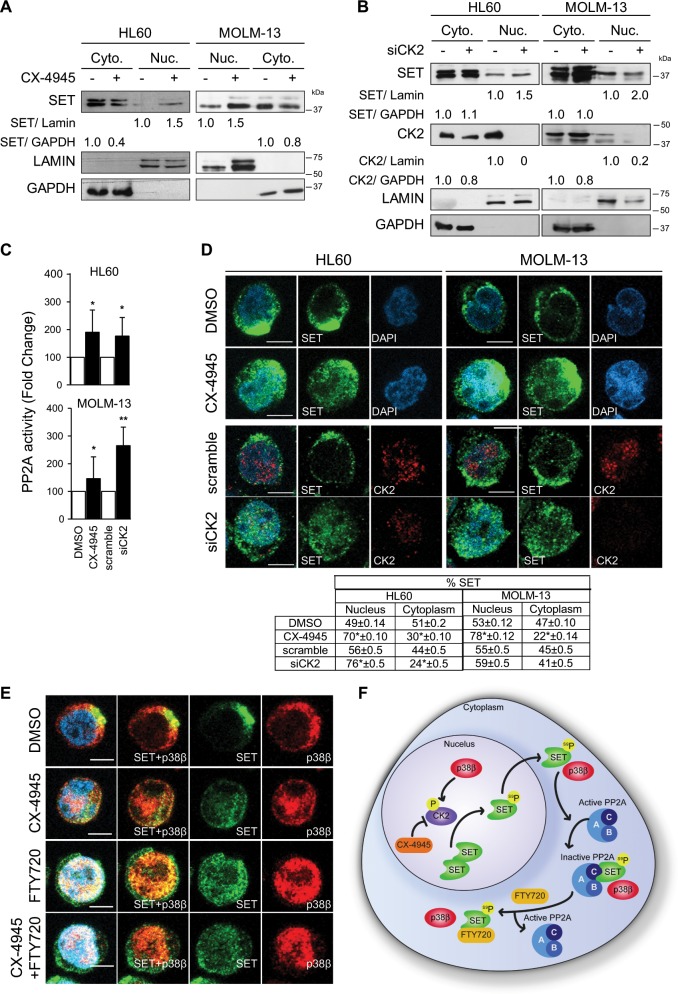
Fig. 5. CK2 inhibition retains SET in the nucleus.
a Nuclear (Nuc.) and cytoplasmic (Cyto.) protein isolated from HL60 and MOLM-13 cells treated with CX-4945 (5 µM, 24 h) and analyzed by western blot for SET localization. b HL60 and MOLM-13 cells treated with specific siRNA for CK2 (20 nM, 48 h). Nuclear (Nuc.) and cytoplasmic (Cyto.) proteins were isolated and analyzed by western blot for SET localization. c Measurement of PP2A activity by immunoprecipitation and phosphatase assay. The results are expressed as fold-change of the control, which are assigned a value of 1 and are mean values ± SEM. Experiments were performed in triplicate four times. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. d Immunofluorescence analysis of CK2 (red) and SET (green). Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Immunofluorescences were visualized by confocal microscopy. Scale bar represents 5 µm. Quantification table of green fluorescence (SET) in nucleus and cytoplasm. The results are expressed as mean values ± SEM. Experiments were performed in triplicate four times. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. e Immunofluorescence analysis of p38β (red) and SET (green). Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Immunofluorescences were visualized by confocal microscopy. Scale bar represents 5 µm. f p38β is able to activate CK2, which phosphorylates SET and, as consequence, facilities SET trafficking to the cytoplasm, contributing to PP2A inactivation in AML cells. Moreover, p38β binds to SET in the cytoplasm, contributing to its stability and leading to PP2A inactivation. Treatment with CX-4945 (CK2 inhibitor) retains SET in the nucleus, avoiding its phosphorylation. FTY720 treatment disrupts the SET-PP2A biding which remains in the cytoplasm.