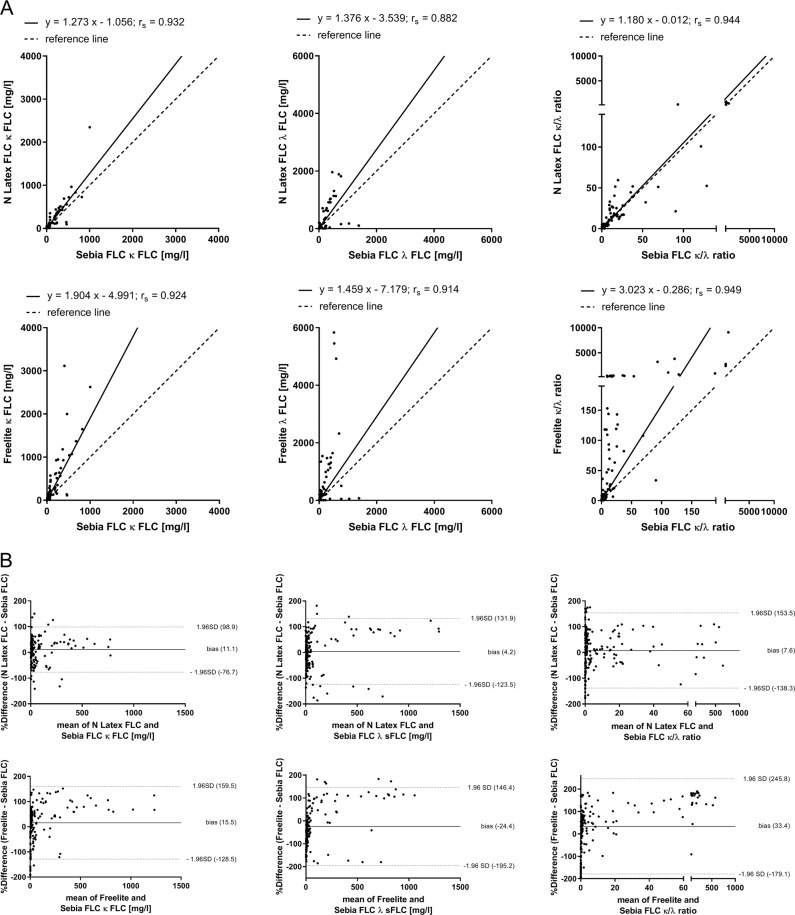
Fig. 2. Comparison of Sebia FLC with N Latex FLC and Freelite in the determination of FLC.
The results of κ and λ FLC and κ/λ ratio determination by Sebia FLC are compared with N Latex FLC and Freelite results using 187 serum samples from patients with newly diagnosed or relapsed multiple myeloma (MM, n = 33), light-chain multiple myeloma (LCMM, n = 8), or smoldering multiple myeloma (SMM, n = 6). Shown are the results of Passing–Bablok (a) and Bland–Altman (b) analyses. Bland–Altman plots indicate agreement between FLC assays. A positive bias indicates higher values for determination of FLC by Freelite or N Latex FLC compared with Sebia FLC. For a better representation of FLC results, four samples with extreme κ FLC results or κ/λ ratios were not shown (sample 1: κ FLC results of Freelite: 14,500 mg/l, N Latex FLC: 11,200 mg/l, Sebia FLC: 3456 mg/l; sample 2: κ FLC results of Freelite: 31,800 mg/l, N Latex FLC: 5880 mg/l, Sebia FLC: 6093 mg/l; sample 3: κ/λ ratios of Freelite: 62,281, N Latex FLC: 727, Sebia FLC: 214; sample 4: κ/λ ratios of Freelite: 27146, N Latex FLC: 605, Sebia FLC: 406).