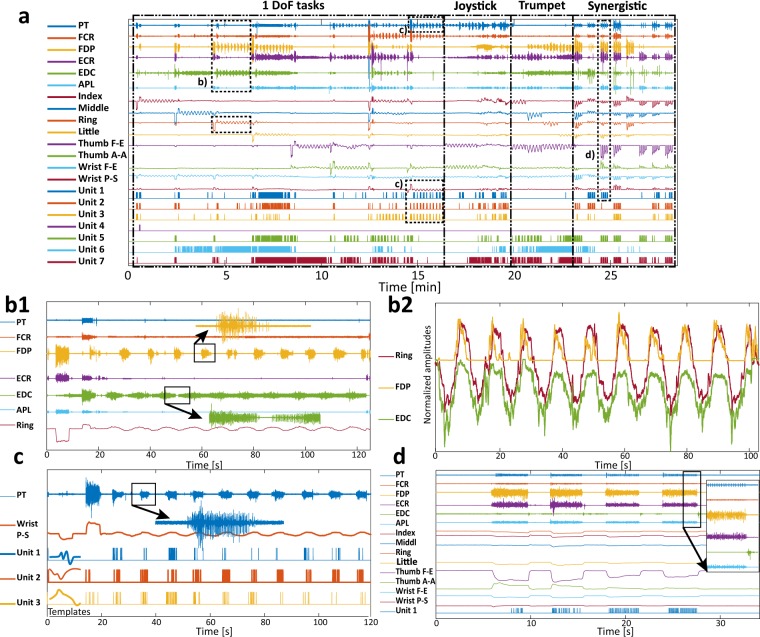
Fig. 2.
Sample of recorded data, subject 7. (a) Recorded signals in one full session: 1–6. iEMG channels (pronator teres – PT, flexor carpi radialis – FCR, flexor digitorum profundus – FDP, extensor carpi radialis – ECR, extensor digitorum communis – EDC, abductor pollicis longus – APL), 7–14 Strain gauges’ outputs. Additionally, activity of 7 muscle units (Unit 1–7) were joined with the recorded signals. The movement groups are separated with dashed lines. To provide more information regarding the recorded signals 4 cases are extracted from this recording and shown in the smaller time window. (b1) This subfigure highlights a single DoF movement. The ring finger force is notably correlated with the FDP and the EDC activities. It could be also noted that during force modulation both firing rate and recruitment of these muscles are changing. (b2) This subfigure illustrates estimation of ring finger force using RMS features of FDP and EDC channels. From the shapes of the time domain signals it could be noted that activity of two antagonistic muscles is reflected in finger force. This correlation is prominent in global trends (increasing/decreasing) of the finger force (increase/decrease), but also in small disturbances of the finger force that are present in iEMG RMS features (c) This subfigure focuses also on a single DoF movement but, besides raw muscle activity the figure also shows extracted spike trains. In the case of activity in the PT, it is interesting that for small forces only single muscle unit was picked-up by the fine-wires so the force modulation is reflected in the firing rate of that MU. The lower part of the subfigure shows three spike templates. (d) This subfigure depicts a synergistic movement that comprises the strong contraction of the majority of the targeted muscles. The aim of this subfigure is to show differences between channels in terms of iEMG content. While in some channels there is only one (or several) MU active, other channels are recording an abundance of MU-s resulting in a signal shape that resembles superficial EMG.