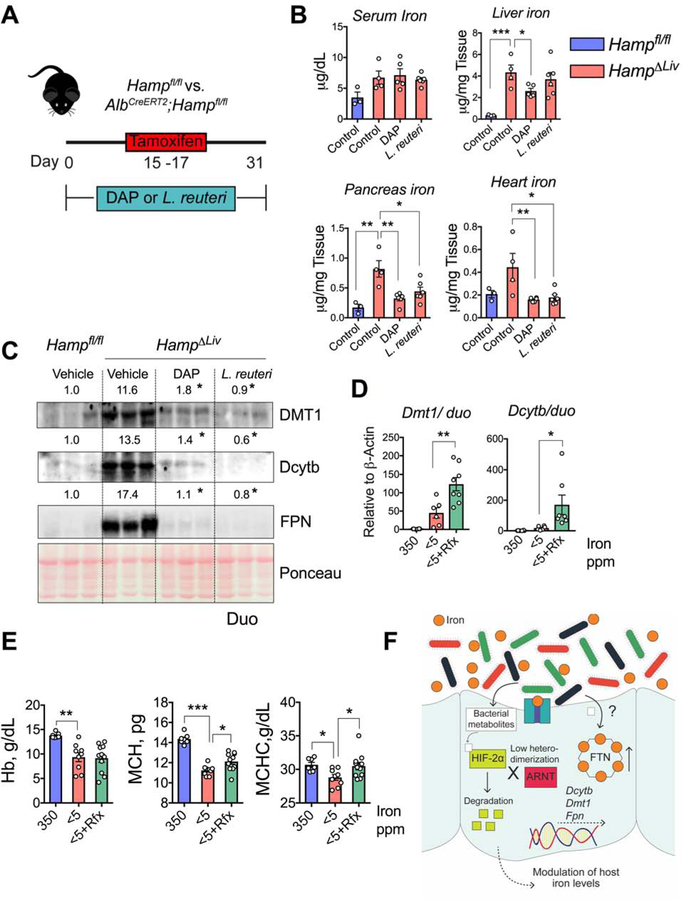
Figure 7. DAP and reuterin prevent systemic iron accumulation and antibiotics improve anemia in mouse models.
A) Schematic showing timeline of DAP or L. reuteri probiotic treatment in tamoxifen-mediated temporal disruption of hepcidin (HampΔLiv). B) Serum and tissue (liver, pancreas and heart) iron analyses and C) Duodenal DMT1, Dcytb and FPN Western analyses in DAP- or L. reuteri probiotic treated Hampfl/fl and HampΔLiv mice. Wild type SPF mice were fed with 350- or <5-ppm iron diet for 1 week followed by 350-ppm, <5-ppm or rifaximin (Rfx) (20 mg/kg/day)-blended <5-ppm diet for another 2 weeks; (D) duodenal Dmt1 and Dcytb gene expression and (E) CBC (Hb, MCH and MCHC) analysis. F) Schematic showing integration of HIF-2α inhibitory and FTN stimulatory roles of gut microbial metabolites to regulate host systemic iron homeostasis. HIF-2α inhibitory metabolites disrupt HIF-2α-ARNT interaction followed by its degradation and subsequent transcriptional downregulation of the intestinal transporters, a different subset of metabolites upregulates FTN expression. Both of these responses can lead to decreased iron absorption.
All data are mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (B, D and E). Western analyses (C): Images were analyzed by Image J software from three independent experiments, representative image shown. Statistical significance compared with Vehicle-only treatment group. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001.