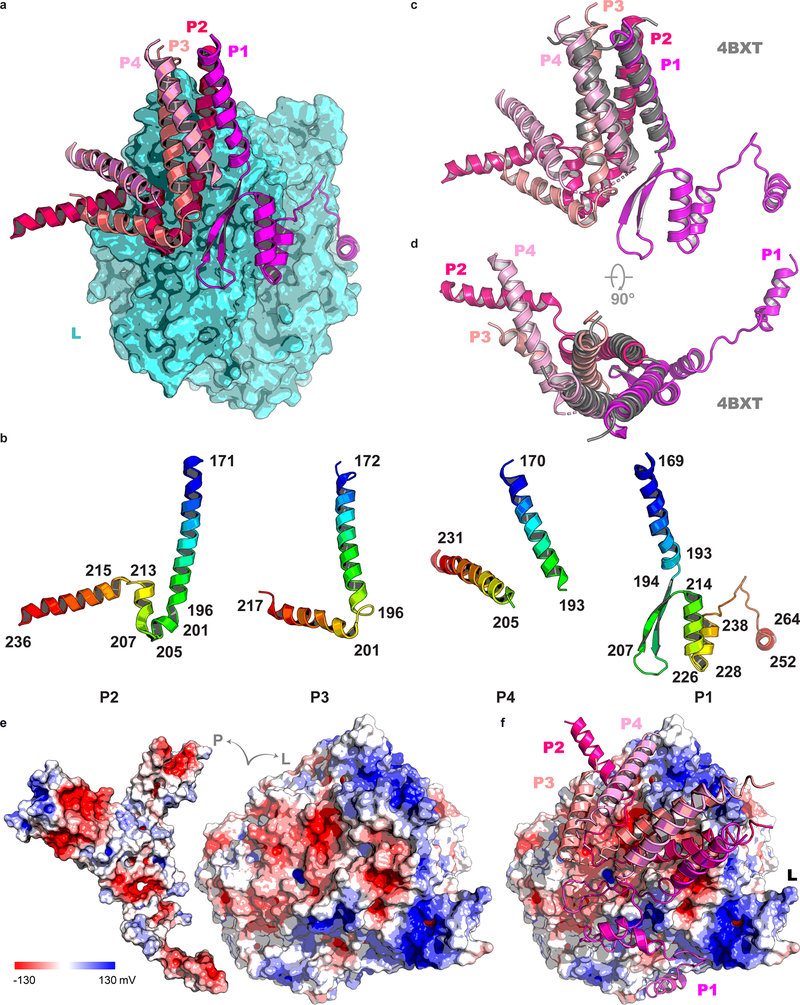
Extended Data Fig. 4 |. Phosphoprotein tetramer in complex with L.
a, The L protein (cyan) is represented as a molecular surface and the tetrameric P protein subunits are represented as ribbons, following the color codes in Figs. 1–3 (P1 in magenta, P2 in hot pink, P3 in salmon and P4 in pink). b, Structures adopted by the four individual P subunits bound to L, colored as a blue to red “rainbow” from the N- to the C- terminal ends. Secondary structures boundaries are noted for each subunit. c and d, Superposition of the tetramerization helices in the context of the L:P complex and the free P protein. Structures are represented as colored ribbons with the free phosphoprotein coiled-coil (PDB access code 4BXT) colored in gray and the four P subunits reported in this work colored according to Fig. 1 (P1 in magenta; P2, hot pink; P3, salmon and P4, pink). The r.m.s.d. of the superimposition is 1.13 Å over 88 α-carbon atoms. e, View of the complex where L and P have been pulled apart to display electrostatic surfaces. f, Overall view of the L:P complex with P shown as ribbons and L as electrostatic surface. The P tetramer consists of subunits P1(magenta), P2 (hotpink), P3 (salmon), and P4 (pink).