-
A–C
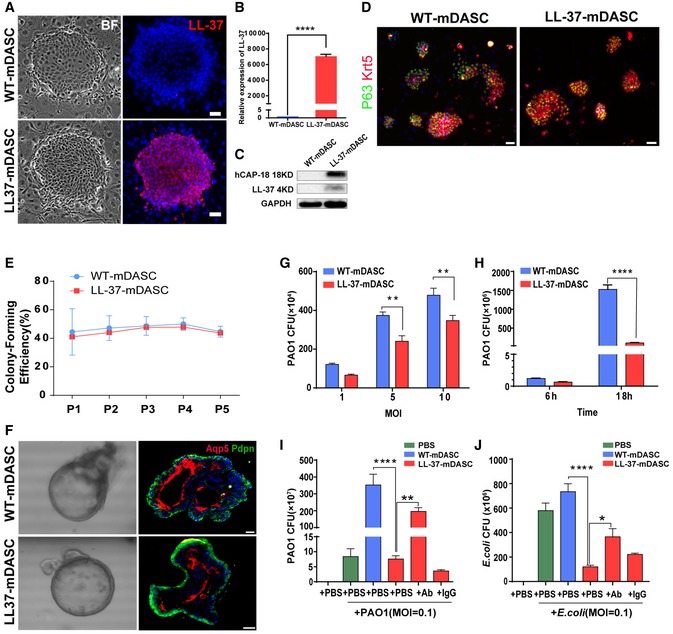
Detection of LL‐37 expression in the engineered mDASCs by immunofluorescence (A), real‐time quantitative PCR (B), and Western blot (C). Scale bar, 50 μm. BF, bright field. n = 10. Error bars, SEM.
-
D
Anti‐Krt5 (red) and anti‐P63 (green) immunostaining of WT‐ and LL‐37‐mDASC colonies. Scale bar, 70 μm.
-
E
Stem cell colony‐forming efficiency of WT‐ and LL‐37‐mDASCs during five serial passages. n = 6. Error bars, SD.
-
F
Representative 3D organoid culture of mDASCs with expression of type I alveolar cell markers (Aqp5 and Pdpn). Left panels, bright‐field imaging of 3D organoids. Right panels, immunofluorescence of organoid sections. Scale bar, 20 μm.
-
G
Co‐culture of bacteria with DASCs shows antimicrobial effects in dose‐dependent manner. Initial additions of PAO1 were 0.1 × , 0.5 × and 1 × 104 CFU, respectively. Co‐culture duration, 6 h. n = 4. Error bars, SEM. MOI, multiplicity of infection.
-
H
Co‐culture of bacteria with DASCs shows antimicrobial effects in time‐dependent manner. Initial concentration of PAO1 was 1 × 104 CFU. MOI = 1. n = 3. Error bars, SEM.
-
I, J
Preincubation of cells with anti‐LL‐37 antibody, but not IgG control, significantly reduced anti‐PAO1 (I) and anti‐Escherichia coli (J) effects of LL‐37‐mDASCs. Initial dose of bacteria was 103 CFU. Co‐culture duration, 18 h. n = 4 in (I) and n = 3 in (J). Error bars, SEM.
‐test (B), two‐way ANOVA followed by Sidak's test (G, H) and one‐way ANOVA followed by Tukey's test (I, J). *
< 0.0001.