Fig. 1. Mutagenicity (no. of revertants) of fermented sausages as affected by six combinations of starter cultures and vitamins treatments.
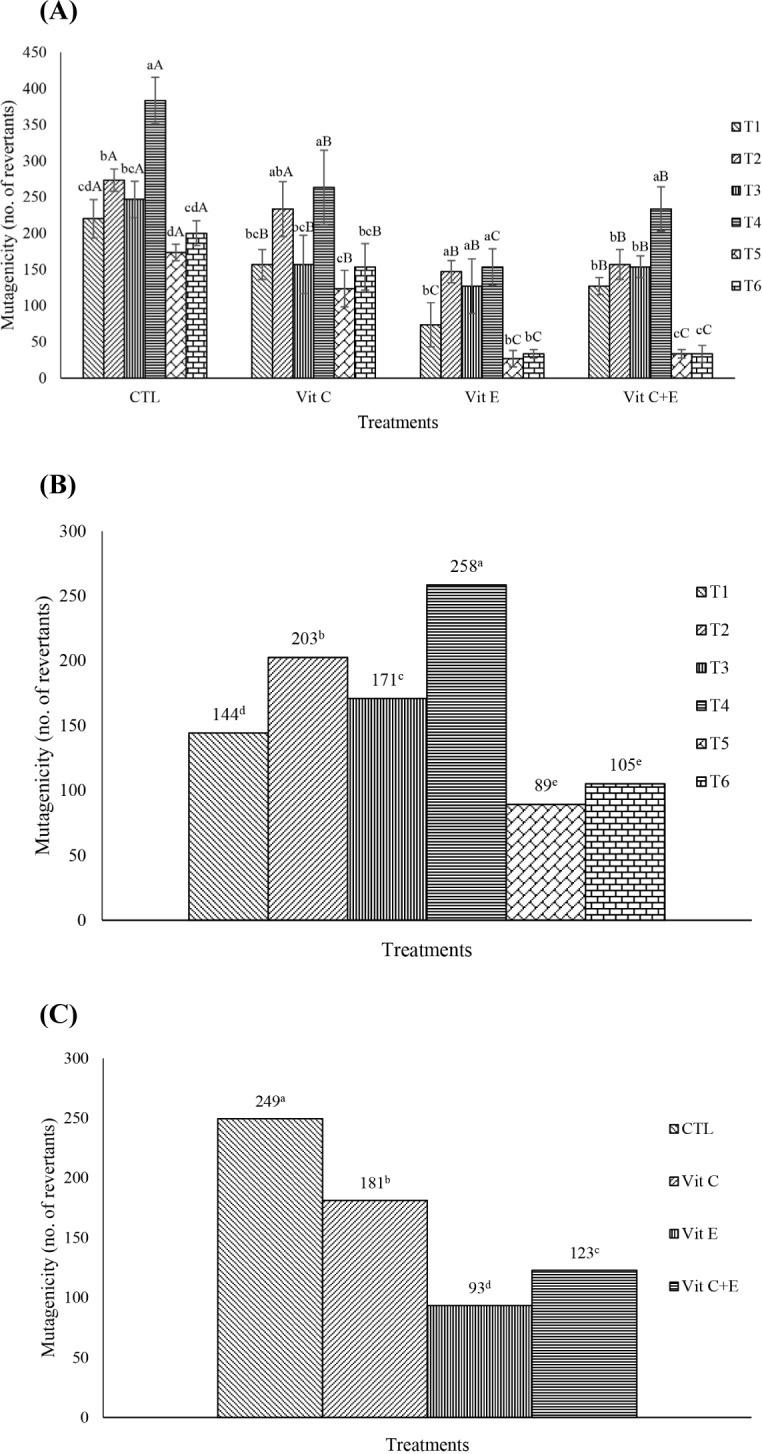
(A) Mutagenicity (no. of revertants) of various fermented sausages. a–d Means with different superscripts within the same treatment are different (p<0.05). A–C Means with different superscripts within the same fermented sausages are different (p<0.05). (B) Mutagenicity (no. of revertants) of six different fermented sausages. a–e Means with different superscripts within the different fermented sausages are different (p<0.05). (C) Mutagenicity (no. of revertants) of fermented sausages treated with vitamins C and E. Treatments are described in Fig. 1A. a–d Means with different superscripts within different treatment are different (p<0.05). Treatments: T1, Pediococcus acidilactici; T2, Pediococcus pentosaceus and Staphylococcus carnosus; T3, Staphylococcus carnosus, Staphylococcus xylosus, Debaryomyces hansenii, Lactobacillus curvatus, and Pediococcus pentosaceus; T4, Staphylococcus carnosus and Lactobacillus sakei; T5, Staphylococcus xylosus and Lactobacillus plantarum; T6, Penicillium nalgiovensis; CTL, fermented sausages (FS) with 6 different starter cultures; Vit C, FS immersed in the same volume of 0.1% Vit C solution; Vit E, FS immersed in the same volume of 0.1% Vit E solution; Vit C+E, FS immersed in the same volume of 0.05% Vit C and 0.05% Vit E solutions.
