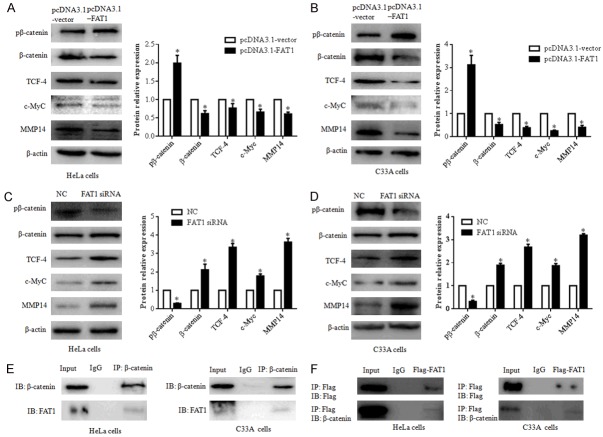
Figure 3.
FAT1 interacts with β-catenin and regulates β-catenin-mediated transcription. (A and B) Overexpression of FAT1 inhibited β-catenin-mediated transcription by phospho-β-catenin (pβ-catenin). pβ-catenin, β-catenin, TCF-4, c-Myc and MMP14 expression levels were evaluated by western blot after transfecting HeLa (A) and C33A (B) cells with the pcDNA3.1-FAT1 plasmid and pcDNA3.1-vector for 48 h, respectively. The histograms illustrate the quantitative analysis of the pβ-catenin, β-catenin, TCF-4, c-Myc, and MMP14 protein levels, which were normalized to the β-actin levels. *P < 0.05, vs. the pcDNA3.1-vector group. (C and D) FAT1 knockdown promoted β-catenin-mediated transcription of HeLa and C33A. pβ-catenin, β-catenin, TCF-4, c-Myc and MMP14 expression levels were evaluated by western blot after transfecting HeLa (C) and C33A (D) cells with NC and FAT1 siRNA for 48 h, respectively. The histograms illustrate the quantitative analysis of the pβ-catenin, β-catenin, TCF-4, c-Myc and MMP14 protein levels, which were normalized to the β-actin levels. *P < 0.05 vs. the NC group. (E) Immunoprecipitation assays detected that endogenous FAT1 bound endogenous β-catenin in HeLa and C33A cells. (F) Immunoprecipitation assays detected that exogenous FAT1-flag bound endogenous β-catenin in HeLa and C33A cells. HeLa and C33A cells were infected with Adv-flag-FAT1 for 48 h. Immunoprecipitation (IP) antibody or immunoglobulin G (IgG) negative controls were used as indicated. β-actin was used as a loading control.