Figure 2.
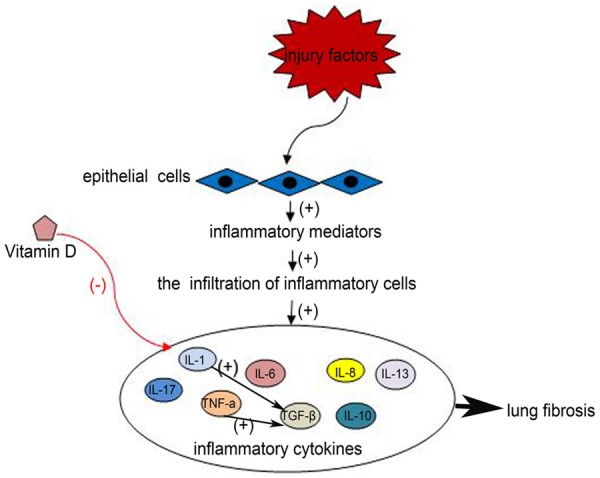
The injured epithelial cells release excessive inflammatory mediators, inducing the sequential infiltration of inflammatory cells. Then inflammatory cells release cytokines (IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-13, IL-17, TGF-β, TNF-α), which promote the inflammatory response and fibrosis. Vitamin D can reduce the levels of inflammatory cytokines, preventing the further expansion of the inflammatory response.
