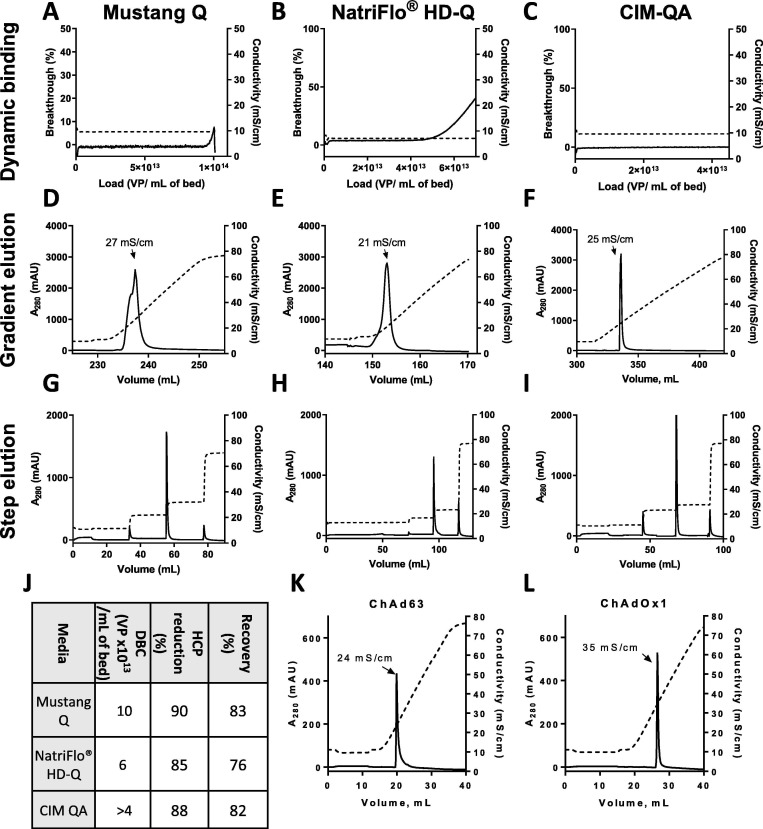
Fig. 4.
Comparison of anion exchange media.
Chromatograms from small-scale anion exchange experiments are shown. In all cases, solid lines indicate A280 (left axis) and dashed lines indicate conductivity (right axis). A260 data was also collected, with results paralleling the A280 data, but is omitted from graphs for clarity.
In panels A-I, each column of graphs represents data from a single type of media, as per column captions. Panels A-F show chromatograms from experiments in which previously purified ChAdOx2 RabG was loaded on Mustang Q Acrodisc, NatriFlo® HD-Q Recon Mini, and CIM-QA 1 mL capsules. In panels A-C. breakthrough was observed and hence dynamic binding capacity was calculated for the Mustang Q and NatriFlo® capsules; breakthrough was not observed after loading 4x1013 VP on the (larger) CIM-QA column. Panels D-F show the continuations of the above experiments, in which virus was eluted using a linear gradient of increasing conductivity to allow estimation of elution conditions; the conductivity at the peak of virus elution is shown.
Panels G-I show chromatograms from experiments in which diafiltered lysate containing ChAdOx2 RabG was loaded on Mustang Q Acrodisc, NatriFlo® HD-Q Recon Mini, and CIM-QA 1 mL capsules, followed by step elution.
Panel J presents DBC, virus recovery and HCP reduction data from the experiments shown in Panels A-F. In the case of the CIM-QA column, breakthrough was not reached despite loading 3x1013 VP on the 1 mL device.
Panels K-L show chromatograms from experiments in which previously purified ChAd63 ME-TRAP and ChAdOx1 RVF were loaded on Mustang Q Acrodisc capsules and eluted with a linear conductivity gradient, as above.