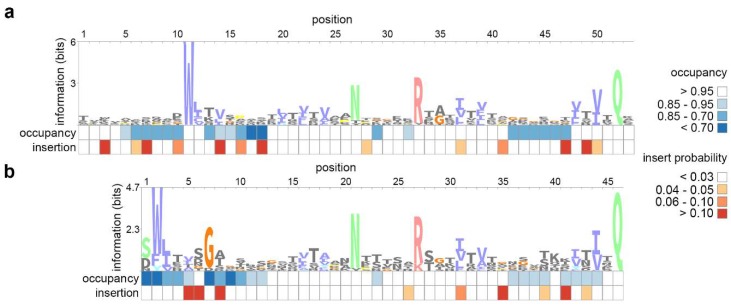
Figure 1.
Sequence logos of Bacteroides-associated carbohydrate-binding often N-terminal (BACON) domain profile hidden Markov models (HMMs) show the divergence between (a) the bacterial BACON domain and (b) the crAssphage-like BACON domain (crAss-BACON). Profile HMMs were constructed from (a) 304 Bacteroidetes domains (PF13004) and (b) domains identified in crAss-like phages. These sequence logos are representations of profile HMMs, which contain probability scores for each amino acid residue at each position in an alignment. In addition, profile HMMs contain probability statistics for insertions and deletions at each position. Occupancy scores denote the probability that an amino acid residue is found at a given position (i.e., low values mean a deletion is more likely to occur at that position). Insertion scores denote the probability of an insertion after a given location. Images were constructed with the Skylign webserver [61,62].