Table 1.
Characteristics of the RCTs conducted within the frame of the PREDIMED study, investigating the role of Mediterranean Diet (MD) on cardiovascular disease (CVD) and cardiovascular risk factors.
| Aim of the Study | Number of Subjects | Follow-Up Median (Years) | Main Results of the Study | 1st Author, Journal, Year |
Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiovascular Disease | |||||
| Incidence of primary endpoint (a composite of CV events: Non-fatal acute myocardial infarction, non-fatal stroke or death from CV causes) |
7447 | 4.8 |
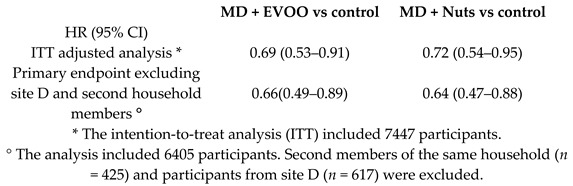
|
Estruch et al. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018 |
[15] |
| Incidence of heart failure | 7403 | 4.8 |
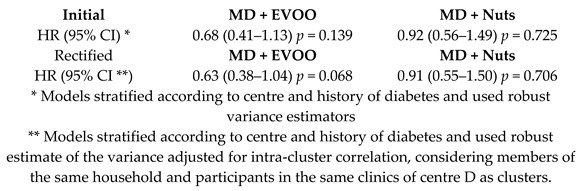
|
Papadaki et al. Eur. J. Heart. Fail. 2017 |
[20] |
| Papadaki et al. Eur. J. Heart. Fail. 2019 |
[21] | ||||
| Incidence of atrial fibrillation | 6705 | 4.7 |
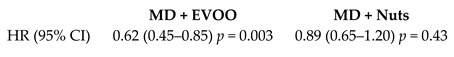
|
Martínez-González et al. Circulation 2014 |
[22] |
| Cardiovascular Risk Factors | |||||
| Long-term consumption of a MD could decrease the atherogenicity of LDL particles | 210 | 1.0 |

|
Hernaez et al. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017 |
[23] |
| Improvement of BP induced by a MD would be mediated by the modulation of NO bioavailability/ET-1 levels | 90 Non-smoking women with moderate hypertension |
1.0 |

|
Storniolo et al. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017 |
[24] |
| Effects of high polyphenol consumption on BP and its relation about production of plasma NO | 200 | 1.0 |

|
Medina-Remón et al. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc Dis. 2015 |
[25] |
| Effects of MD on inflammatory biomarkers related to atherosclerosis and plaque vulnerability | 164 | 1.0 |
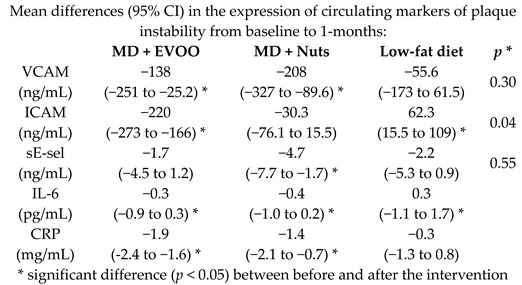
|
Casas et al. PLoS ONE 2014 |
[26] |
| MD effect on 24-h ambulatory BP, blood glucose, and lipids | 235 | 1.0 |
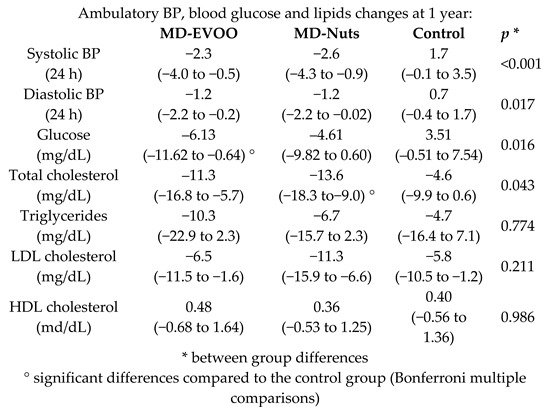
|
Doménech et al. Hypertension 2014 |
[27] |
| Effect of the MD on heart failure biomarkers | 930 | 1.0 |
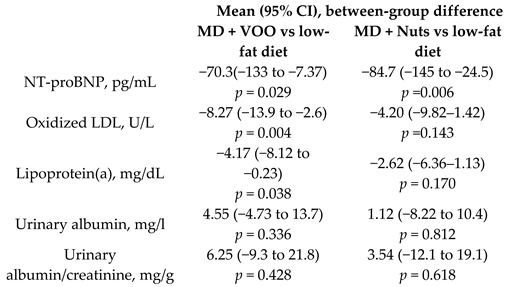
|
Fitó et al. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2014 |
[28] |
| Incidence of Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) | 7435 | 4.8 |

|
Ruiz-Canela et al. JAMA 2014 |
[29] |
| Effects of MD on BP | 7158 | 3.8 |

|
Toledo et al. BMC medicine 2013 |
[30] |
| Effects of MD on progression of subclinical carotid atherosclerosis |
187 | 1.0 |

|
Murie-Fernández et al. Atherosclerosis 2011 |
[31] |
| The short-term effects of MD versus those of a low-fat diet on intermediate markers of CV risk. |
772 | 0.25 |
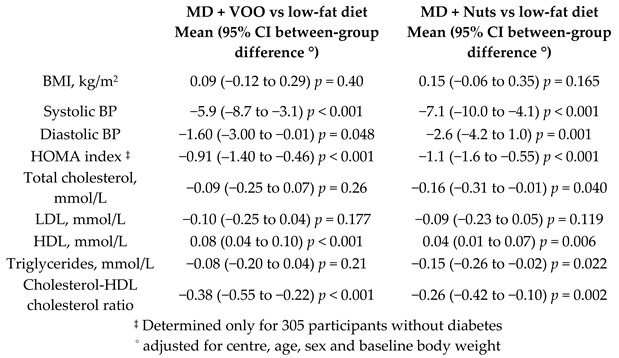
|
Estruch et al. Ann. Int. Med. 2006 |
[32] |
BMI: Body Mass Index; BP: Blood Pressure (mmhg); CV: Cardiovascular; MD: Mediterranean Diet; ET-1: Endothelin 1; EVOO: Extra Virgin Olive Oil; HDL: High-Density Lipoprotein; HOMA: Homeostatic Model Assessment; ICAM: Soluble İntercellular Adhesion Molecule; IL-6: İnterleukin 6; IMT: Intima-Media Thickness; LDL: Low-Density Lipoprotein; MCP-1: Monocyte Chemotactic Protein 1; NO: Nitric Oxide (Um); NT-proBNP: N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide; Se-Sel: Soluble E Selectin; TNF- Α: Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha; VCAM: Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule; VOO: Virgin Olive Oil.
