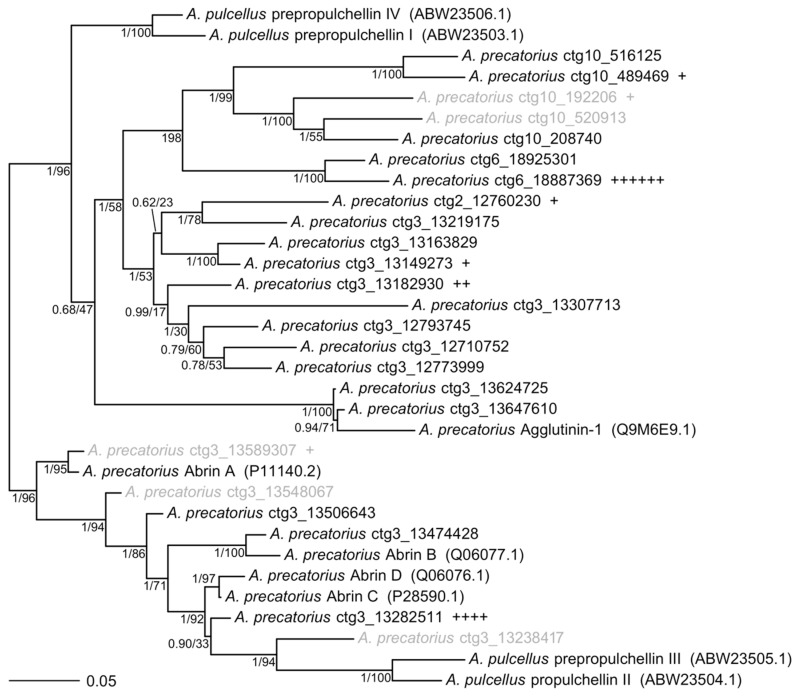
Figure 2.
Unrooted phylogenetic tree of Abrus abrin and prepropulchellin protein sequences. Independent maximum likelihood (ML) and Bayesian analyses estimated the same tree topology with the exception of the poorly supported placement of ctg3_13282511. Numbers indicate ML bootstrap values and Bayesian posterior probabilities, respectively. Branch lengths and topology shown are from the Bayesian estimation. Novel sequences are denoted with contig number (“ctg”) and start codon position within genome assembly reported in this work (NCBI: GCA_003935025). Each instance of an individually sequenced isoform mapped to each sequence is denoted by a plus sign (18 total abrin-like isoforms were identified from the Iso-Seq sequencing). Accession numbers for reference sequences are included in parentheses. Sequences in gray indicate putative pseudogenes. Genes used in this comparison include Abrin A, Abrin B, Abrin C, Abrin D, prepropuchellin I–IV, and Agglutinin genes published on NCBI GenBank (Tables S1 and S2). The translated alignment file used to generate this tree is available (File S1).