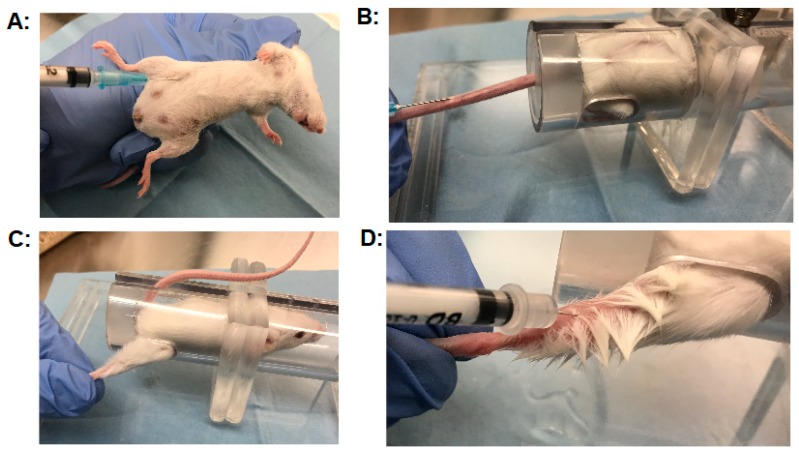
Figure 2.
Mouse Injection techniques: (A) Intraperitoneal (IP) injections: The mouse is restraint in one hand by holding the scruff of the neck tightly between thumb and forefinger and the tail between pinky and palm of the hand and injected into the lower right quadrant of the peritoneum. (B) Intravenous (IV) injection: The mouse is restraint in a tube-like restraining device, with the tail being extended through a hole at the end of the tube. The tail vein is easily visible and is injected by inserting a needle into the vein at a shallow angle. (C) Restraint of a mouse for intramuscular injection into the right hind limb. (D) Intramuscular (IM) injection into the gastrocnemius muscle: The hind limb of the mouse is gently stretched, and the gastrocnemius muscle is injected with a small 30 gauge needle, inserting the needle to about themidpoint of the muscle. All animal experiments have been approved by the University of Wisconsin Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC).