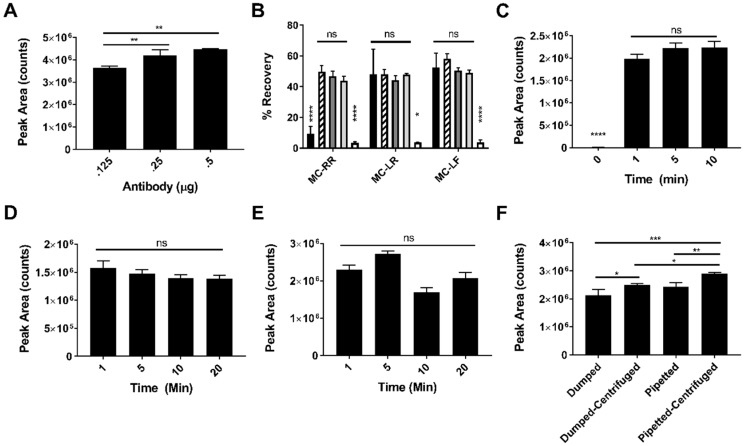
Figure 2.
MC-LR immunocapture (IC) optimization. All optimization experiments were performed using 500 µL of 1 ng/mL singly-charged (MC-LR) congeners in pooled urine. In panel B, 500 µL of 1 ng/mL doubly-charged (MC-RR) and uncharged (MC-LF) congeners in pooled urine were also used. MC antibody titration to optimize capture of MC-LR from pooled urine (n = 3) (A). Selection of optimal elution buffer for IC of three MC congeners. Black bar (100% ACN/0.5% FA), striped bar (70% ACN/30% water/0.5% FA), dark gray bar (50% ACN/50% water/0.5% FA), light gray bar (30% ACN/70% water/0.5% FA), white bar (100% water/0.5% FA), (n = 3) (B). Capture time optimization for antibody conjugation to magnetic beads (n = 3) (C). Capture time optimization of MC-LR from pooled urine (n = 3) (D). Time optimization for eluting MC-LR from magnetic beads (n = 3) (E). Optimal conditions for removing supernatants from beads (n = 3) (F). Significance was determined by one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparisons post-test. * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.0005, **** p ≤ 0.0001, ns = not significant. Error bars represent the standard deviation of replicate samples. % Recovery = peak area of pre-spike sample/peak area of post-spike sample × 100%.