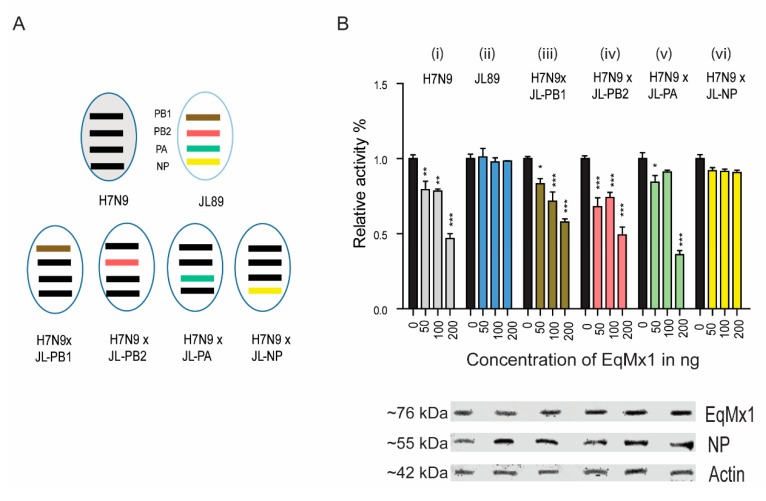
Figure 3.
The viral NP is responsible for the sensitivity to eqMx1. (A) Schematic representation of the assortment of viral polymerases. The four polymerases (PB1, PB2, PA, and NP) from chicken H7N9ZJ13 were swapped one by one with the equivalent polymerases from A/equine/Jilin/1/1989 (H3N8JL89), and each group of assorted plasmids was co-transfected into HEK293T. (B) Relative Luciferase activities of combination sets of IAV against eqMx1. Cells were co-transfected with expression plasmids of the polymerase PB1 (40 ng), PB2 (40 ng), PA (20 ng), and NP (80 ng) in six different groups, (i) all polymerases of H7N9ZJ13, (ii) all polymerases of H3N8JL89, (iii) PB2, PA, NP of H7N9ZJ13 and PB1 of H3N8JL89, (iv) PB1, PA, NP of H7N9ZJ13 and PB2 of H3N8JL89, (v) PB1, PB2, NP of H7N9ZJ13 and PA of H3N8JL89, (vi) PB1, PB2, PA of H7N9ZJ13 and NP of H3N8JL89, together with 40 ng of minigenome reporter (FF-luc) and 10 ng of Renilla luciferase expression plasmids (pRL-TK, as an internal control) in the presence of HA-tagged pcDNA-3.1 eqMx1 or an empty control vector at an increasing concentration 0, 50, 100, and 200 ng each. After 24 hr of transfection, cells were lysed using a 1X reporter lysis buffer. Firefly and Renilla luciferase activities were measured. The resulting relative activity in the presence of either H7N9ZJ13 or H3N8JL89 was set to 100%. The western blot analysis shown in (B) was performed to determine the expression levels of eqMx1 and NP. (Statistical differences between samples are indicated, according to a one-way ANOVA followed by a Dunnett’s test; NS = not significant, * 0.01 ≤ p < 0.05, ** 0.001 ≤ p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. Error bars represent the SEM within one representative experiment).