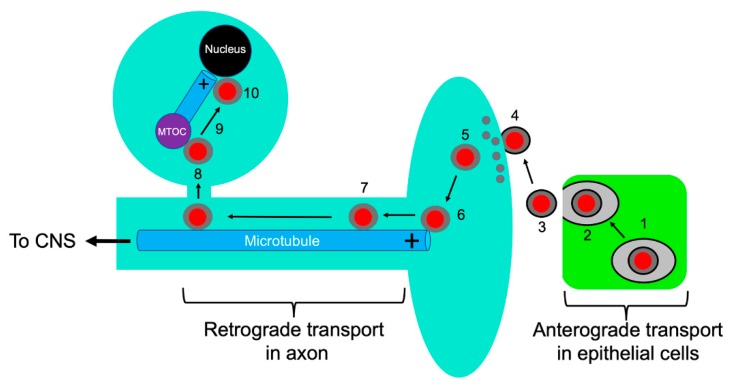
Figure 1.
Alphaherpesvirus entry into neurons. Capsids are represented as red discs and the UL36p/UL37p inner tegument as a gray capsid-bound layer. Microtubules are blue rods with the + end indicated. Virions replicate and assemble in infected epithelial cells (green) (1) and exocytosis (2) releases infectious enveloped particles (3) that fuse at the surface of adjacent sensory neurons (4). Tegument partially disassembles (grey discs) (5), and the capsid with associated inner tegument attaches to the plus end of axonal microtubules (6). The tegument-bound capsid then recruits dynein/dynactin and proceeds by MT-directed retrograde axonal transport (7), eventually reaching the MTOC (purple disc) (8). The capsid then switches to an anterograde trafficking mode (9) to deliver the viral genome to the cell nucleus (10).