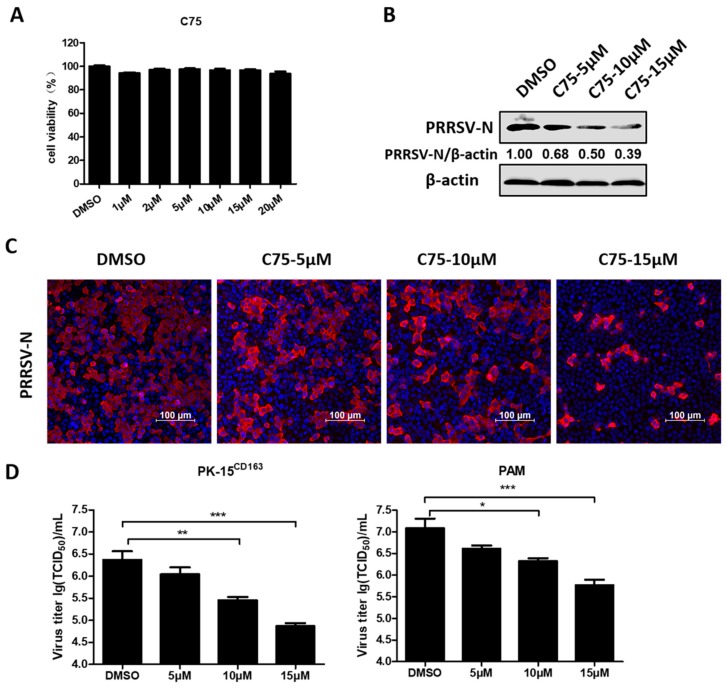
Figure 1.
The pharmacological inhibitor (C75) inhibited porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) replication. (A) PK-15CD163 cells were incubated with various concentrations of C75 or DMSO, as a control, for 30 h for the 3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5 diphenyl-2H-tetrazoliumbromide (MTT) assay to determinate the cytotoxicity of C75. (B) PK-15CD163 cells were pretreated with C75 at the indicated concentrations (5, 10, and 15 µM) for 6 h. The cells were then infected with PRRSV (MOI = 0.5) in the presence of indicated concentrations of C75 and harvested at 24 h post-infection (hpi) for western blot assay, using a specific antibody against PRRSV-N protein. β-actin was used as a loading control. (C,D) Indirect immunofluorescence assay (PRRSV-N, red; nuclei, blue) (C) and TCID50 assay (D) were separately performed to determine the expression levels of PRRSV-N protein, virus titers in PK-15CD163, or porcine alveolar macrophages (PAMs) treated with C75 as described in (B). Data are expressed as means and standard deviations from three independent experiments. *, 0.01 ≤ p < 0.05; **, 0.001 ≤ p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.