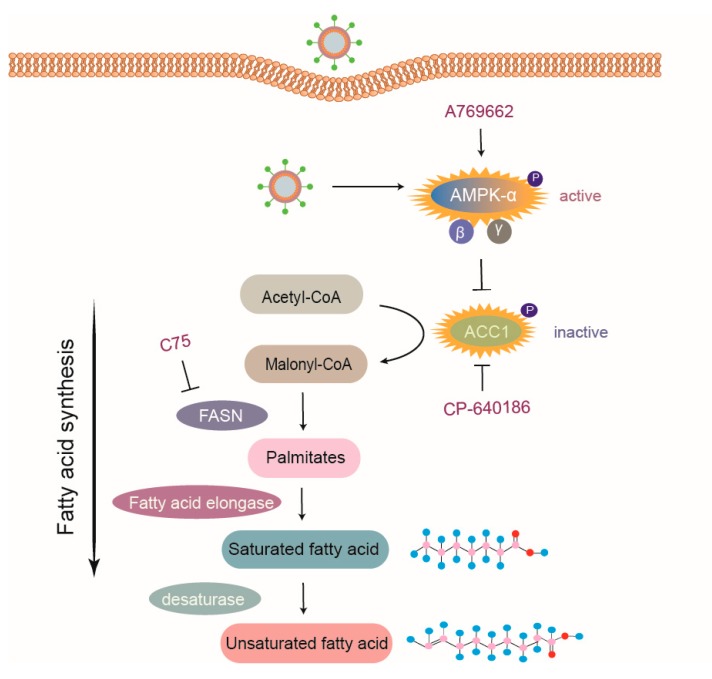
Figure 7.
Model of PRRSV-mediated manipulation of the AMPK–ACC1 pathway. Acetyl-CoA is metabolized to malonyl-CoA via ACC1, which is then transformed into palmitates by FA synthase (FASN). Palmitates are prolonged through FA elongase to form saturated FAs, which are subsequently metabolized to unsaturated FAs by desaturase. PRRSV infection activated AMPK, thus resulting in an increased level of phosphorylated ACC1 (inactive form) to block FA synthesis. Pharmacological agents targeting various steps of FA synthesis pathway, such as C75 (inhibitor of FASN), CP-640186 (inhibitor of ACC1), and A769662 (activator of AMPK), suppressed FA biosynthesis and subsequently inhibited the replication of PRRSV. In summary, host cells limit PRRSV infection via the AMPK–ACC1 pathway.