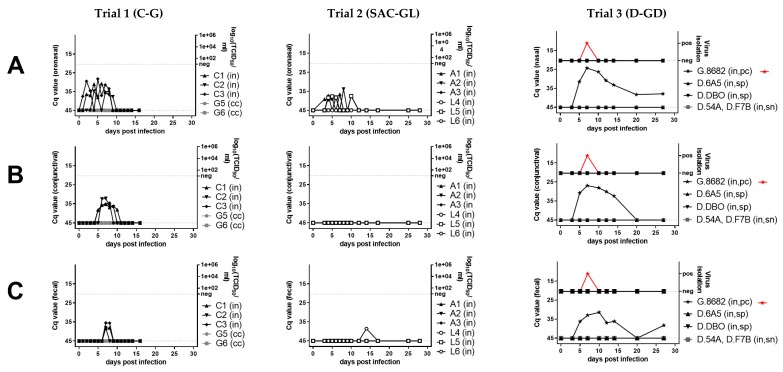
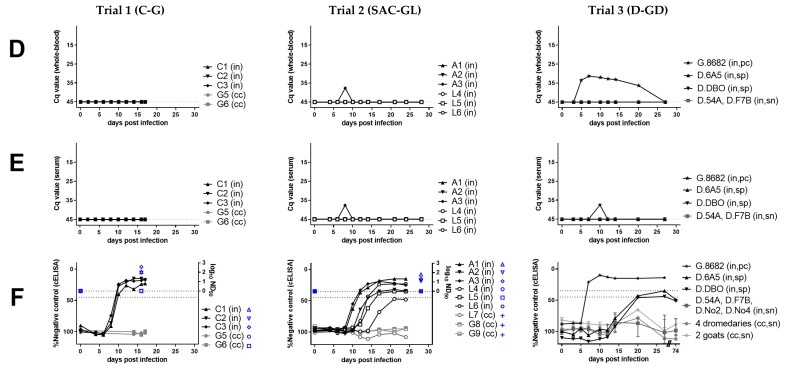
Figure 1.
Virological (A–E), serological (F), hematological (G), and clinical (H–I) results of peste-des-petits-ruminants virus (PPRV) transmission trials after intranasal experimental infection (in) of three cattle (C, trial 1), six South American camelids (SAC, trial 2) (three alpaca (A) and three lama (L)), six dromedaries (D) and one positive control (pc) goat (G) (trial 3) with PPRV lineage IV strain Kurdistan/2011 [41]. Panels belonging to anyone of the three trials are shown from top to bottom (trials 1A–I, trial 2 A–I, trial 3A–I). Panels from left to right show samples by trial analyzed with the same methods. (A) PPRV or PPRV-RNA loads in oronasal swabs, (B) PPRV or PPRV-RNA loads in conjunctival swabs, (C) PPRV or PPRV-RNA loads in fecal swabs, (D) PPRV-RNA loads in whole-blood, (E) PPRV-RNA loads in serum, (F) PPRV antibody levels or neutralizing antibody titers in serum, (G) proportion of white-blood-cells (WBC) relative to day 0 (before infection), (H) clinical score values, (I) rectal body temperature values. For samples from trials that were additionally analyzed by virus titration (TCID50/mL), virus isolation (red symbols) or neutralization test (ND50) (blue symbols) the respective analysis is given on the y-axis of the graphs. PPRV could not be isolated from any of the cattle or camelids, but PPRV was isolated from the positive control (pc) goat (G.8682) (red symbols) of the dromedary trial. In the panels f and g of trial 3, individual results were presented for dromedaries that seroconverted (seropositive, sp) and the positive control (pc)-goat, while median and range values of dromedaries (n = 4) that remained refractory (seronegative, sn) to intranasal (in) PPRV-inoculation and of contact control (cc) dromedaries (n = 4) and goats (n = 2) are shown to allow a clearer overview of the data. Cq, quantitative cycle value of PPRV-RNA quantified by real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (RT-qPCR) with the PPRV-assay of Batten et al. 2011 [50]; TCID50/ml, 50% tissue culture infective dose obtained by virus titration assay using vero.dog.SLAM.tag cells [43] or CHS-20 (goat-SLAM) cells [42] (both cell lines show a similar sensitivity for virus isolation from different animal species [9]; cELISA, competition ELISA (IDvet); ND50, virus neutralization by PPRV antibodies in 50% of the replicates.