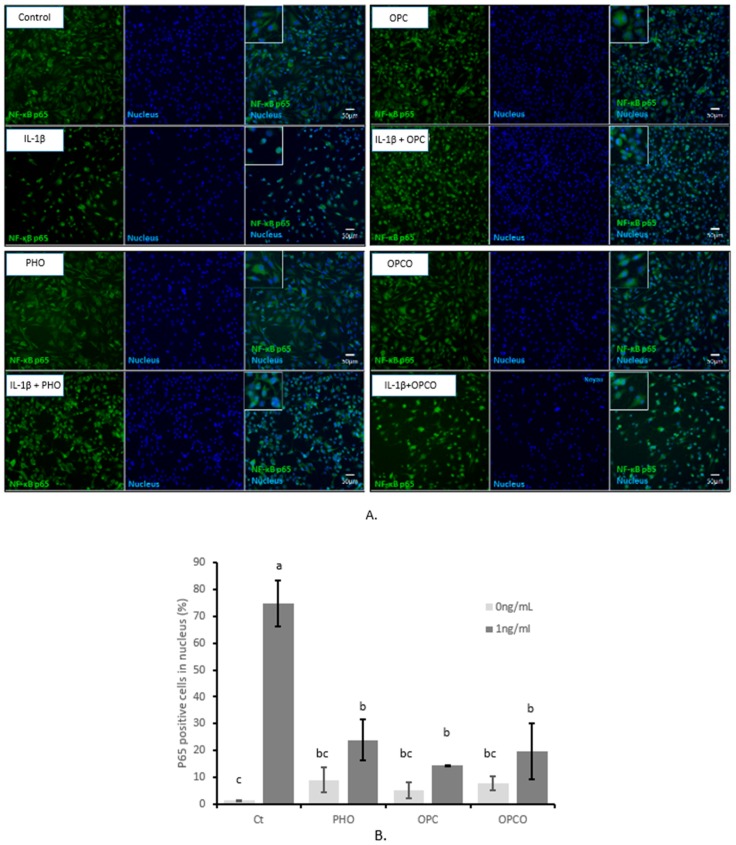
Figure 3.
PHO, OPC, and OPCO effects on the IL-1 β-dependent nuclear transcription factor-kappa B (NF-κB) p65 translocation in human articular chondrocytes: Human articular chondrocytes (HACs) were harvested from tibial plateau and femoral condyles following knee replacement surgery and isolated. Extracts were dissolved in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium high glucose (DMEM) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Illkirch, France). Solutions were sterilized by filtration through 0.22-µm membranes. Cells were preincubated with PHO, OPC, or OPCO extract solutions at 10 µg/mL for 24 h and stimulated with IL-1 β (1 ng/mL) for additional 24 h. Immunofluorescence assay for p65 subunit (A) was performed, and p65 positive cells in nucleus was counted (B). PHO, OPC, and OPCO extract solutions limited IL-1 β-induced p65 translocation to the nucleus. PHO, OPC, or OPCO extracts are characterized for their content in hydroxytyrosol, procyanidins, or both. Groups with significant differences (P < 0.05) are indicated with different letters (a, b and c).